In online marketplace platforms, data analytics and user behavior analytics are the Holy Grail, providing companies with insights that can inform decisions and drive marketing, improve customer experiences, and grow their businesses through data-driven marketplace optimization.
Leveraging Data Enables Businesses To:
- Understand Customer Behavior – Understand user behavior and purchasing habits.
- Optimize Marketing – Monitor and enhance campaign performance.
- Identify Market Trends – Discover new opportunities and shifts in advance.
- Enhance Customer Experience – Personalized messaging and offers.
- Drive Growth – Make strategic decisions for long-term success.
Understanding Two-Sided Marketplaces and Their Unique Challenges
A 2-sided marketplace platform is one that brings two different sets of users, often consumers and service providers, together and enables them to interact and exchange with one another.
These are platforms like Uber, where service providers, drivers, provide rides to passengers, the consumers. There is also Airbnb, where service providers, hosts, lease their buildings to guests, the consumers.
Some common categories of marketplace platforms include:
- Hiring websites like Indeed/Naukri help with union of employers and candidates.
- Freelance platforms such as Upwork connect companies and freelancers.
- Ride-sharing companies such as Uber link riders and drivers.
Most two-sided marketplaces make money by levying a commission to facilitate transactions between consumers and service providers. Consider, for instance, all the various Zomato service fees that are added to your $15 pizza delivery. Some marketplaces, such as Naukri, make money by charging one side, i.e., the employers, and making the other, job seekers, free.

Harnessing Data to Power Two-Sided Marketplaces
In 2-sided markets, data analytics has a driving impact on keeping supply and demand in balance, delivering continuous improvement in user experience, and enabling sustainable growth. Utilizing knowledge of user behavior analytics, transaction patterns, and predictive analytics in marketplaces, platforms can improve personalization, anticipate demand, and optimize pricing dynamically.
Let's further explore this blog on building transaction analytics platforms and creating data analytics marketplaces. Companies can develop data-driven business models (DDBMs) to identify value and solidify strategic partnerships through robust data engineering services.
While data is a powerful enabler, platforms also have to overcome some very severe challenges, including managing supply and demand, guaranteeing quality, avoiding platform leakage, and beating their competitors.
Key Components of a 2-Sided Marketplace Platform
2-sided platforms have some elements in common. Let’s examine the anatomy of a two-sided marketplace and the core components that make it happen.
The primary user groups: Consumer & Service Providers
At the heart of any thriving marketplace, online or offline, are the two primary user groups: the consumers and the service providers. These people generate almost all the activity on the platform, engaging in a continuous dance of supply and demand.
Consumer
These are users in search of a particular product or service. They come to the marketplace platform for the convenience, the options, and the competitive prices.
But it’s not just about scoring a sweet deal. Consumers also enjoy a sense of trust and security that comes with purchasing through an established data-driven marketplace. For instance, protection policies help ease any worries.
Platforms cater to this by simplifying purchasing with consumer tools like:
- Search filters to quickly discover listings.
- Sorting to view products by price, ratings, etc.
- Secure payment processing.
- Review systems to identify quality service providers.
- Protection/refund policies.
Generally, users have to register accounts and provide a little bit of information: name, payment details, etc. Other marketplaces might also ask for the shipping address or the preferred method of communication.
Service Providers
The platforms themselves are service providers. These could be individual vendors, or they could be corporations looking to advertise and sell their merchandise to wider audiences.
Service providers typically must provide account information and details about the type of business they operate, the goods or services they provide, and payment information, just as consumers do. They also potentially have convenient tools to manage listings, speak to customers, and manage sales using insights from marketplace analytics.
Key features for service providers include:
- Self-service dashboards to manage listings, inventory, and orders.
- Promotional tools, like coupons, to boost sales.
- Communication channels to interact with customers.
Reporting to gain insights into product performance using marketplace data insights.
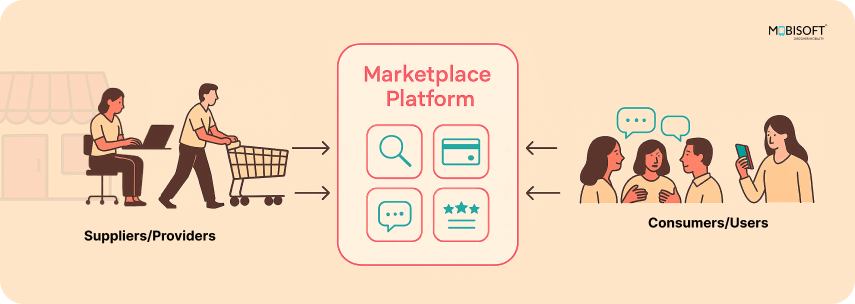
The role of the platform in facilitating interactions
At the heart of any two-sided market lies the platform. It facilitates the meeting of consumers and service providers. It creates value in the sense that it provides the means and the trust to facilitate significant transactions, an essential part of any two-sided marketplace strategy.
Key responsibilities include:
- Marketing Tools – Helping service providers reach the right consumers through targeted promotions.
- Payment Processing – Managing secure, streamlined transactions with purchase protection.
- Trust & Safety – Establishing trust based on features such as authenticated profiles, user ratings, and open policies.
- Dispute Resolution – Helping both sides by resolving disputes timely and fairly.
In short, the offers an end-to-end experience from discovery through post-sales support, and the order is kept in place by controls, governance, and rules.
The Role of Data Analytics in Optimizing 2-Sided Marketplaces
For an online marketplace platform where buyers and sellers meet, information determines growth, personalization, and performance. It also supports customer acquisition in marketplaces, builds trust, enables better pricing, and guides critical decisions.
Types of data relevant to 2-sided marketplaces
User behavior data (consumers and service providers):
Understanding how consumers and service providers interact with your platform is crucial. This includes:
- Clicks, scrolls, time spent on pages
- Product/service views
- Wishlist additions or “favorites”
- Response time (from service providers)
- Abandonment rates (for consumers)
Why it matters
Behavioral data powers personalization, simplifies onboarding, and helps identify friction points in the user experience, supporting better retention strategies marketplace-wide.
For implementation reference, you can explore the Google Analytics 4 (GA4) Guide to understand how to collect and analyze user behavior effectively.
Transaction data:
- Volume of completed transactions.
- Average order value (AOV).
- Conversion rates (visitor to consumer).
- Service provider performance metrics (fulfillment rate, cancellation rate).
- Refund and dispute rates.
Why it matters
Marketplace conversion rate analytics help fuel loyalty programs, detect anomalies, and improve operational efficiency.
Market trends and competitive analysis:
- External market data (e.g., pricing benchmarks, industry reports).
- Seasonality and demand shifts.
- Geographic behavior differences.
- Competitor pricing and offerings.
Why it matters
These insights are foundational for product strategy, price sensitivity analysis, and inventory control, as covered in E‑commerce Analytics: The Ultimate Guide to Growing Your Online Store.
Importance of Data Collection and Management.
An effectively governed marketplace platform is a data-driven engine. Let's see how the collection of structured data and effective data governance are important for driving growth in data analytics
- Personalization: Suggesting products or service providers based on behavior history.
- Trust & Safety: Fraud detection algorithms need quality, real-time data.
- Dynamic Pricing: Supply/demand-based pricing models improve margins.
- Growth Analytics: Understand which levers (marketing, referral, promotions) drive user acquisition and retention.
Feedback Loops: Structured reviews and ratings enrich decision-making for both sides.
Marketplace Optimization Using Analytics Techniques
Data analytics achieves its complete worth when it is utilized not only for comprehending the past but for creating the future, especially when platforms embrace Self-Service Analytics: What Is It and Why Is It Important? to enable faster, decentralized decision-making. In two-sided markets, applying the appropriate analytics techniques powers everything from user experience to pricing strategy and operational efficiency.
Analytics techniques that can be applied:
Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics is concerned with explaining historical data, recognizing patterns, and trends.
Use Cases:
- Understanding top-selling categories or services
- Analyzing user acquisition and churn
- Segmenting consumers and service providers based on user behavior analytics
- Measuring campaign performance
Example: A weekly dashboard showing the number of active service providers, consumer transactions, and conversion rates supports marketplace tracking and optimization.
Predictive Analytics
Forecasting future trends and user behaviors.
Definition: Predictive analytics uses historical data and machine learning to forecast future outcomes.
Use Cases:
- Forecasting demand for products or services
- Predicting churn (when users are likely to leave the platform)
- Anticipating fraudulent transactions
- Estimating the lifetime value (LTV) of users
Example: A churn prediction model identifies which service providers are likely to become inactive and triggers automated re-engagement emails, supporting retention strategies marketplace-wide.
Prescriptive Analytics
Recommending actions based on data insights.
Definition: Prescriptive analytics suggests specific actions based on predictive models and optimization algorithms.
Use Cases:
- Recommending dynamic pricing adjustments
- Allocating marketing budget across acquisition channels
- Matching consumers and service providers more efficiently
- Suggesting supply-side improvements (e.g., inventory or listing enhancements)
Example: A system recommends a price drop for a listing based on the current supply and demand imbalance, a practice powered by marketplace analytics.
For businesses looking to adopt advanced forecasting and automation, exploring AI strategy consulting & machine learning services can further accelerate results.
Tools and Technologies for Marketplace Data Analytics (e.g., Google Analytics, Tableau, custom dashboards)
| Tool | Use Case | Strength |
| Google Analytics / GA4 | Web traffic, conversion funnels | Easy to implement, great for frontend tracking |
| Tableau / Power BI | Visual dashboards | Drag-and-drop visualizations, great for stakeholders |
| Mixpanel / Amplitude | User behavior analysis | Deep cohort analysis and funnel tracking |
| Looker / Metabase | Custom dashboards on top of databases | Data modeling, SQL-friendly |
| Custom Solutions | Real-time analytics, predictive models | Flexibility, integrated deeply with product logic |
Key Areas to Optimize Using Data & Analytics
Data is not just for reporting; when applied effectively, it becomes a tool for continuous optimization across every part of a two-sided marketplace strategy. Let’s explore how insights derived from data analytics for marketplace optimization enhance platform performance:

User Experience
Creating a seamless and intuitive experience is critical in retaining both consumers and service providers.
Personalization Based on User Behavior
- Tailor homepage content, search results, or product recommendations based on past user behavior.
Example: If a consumer frequently views handmade jewelry, prioritize similar listings in their feed.
A/B Testing for Continuous Improvement
- Test interface changes (e.g., button placement, CTA copy, onboarding flows) with controlled user groups.
- Analyze metrics like click-through rate (CTR), conversion, and retention to determine the winning variant.
Impact: Increases engagement, reduces bounce rates, and improves conversion by continuously aligning UX with user expectations.
Learn how mobile-first platforms are transforming personalization with Mobile App Analytics: Key to Building Successful Apps.
Pricing Strategies
Correct pricing influences consumer demand and service provider participation, especially in marketplaces with fluctuating supply and demand.
Dynamic Pricing Models
- Adjust prices based on availability, time of day, user demand, and competitor rates.
Example: A ride-hailing app increases prices during peak hours using real-time analytics for marketplaces to match demand.
Competitive Pricing Analysis
- Monitor competitors or similar listings to benchmark price points.
- Use this to suggest optimal pricing for service providers or automatically adjust platform fees.
Impact: Improves marketplace efficiency, boosts service provider revenue, and enhances consumer satisfaction by ensuring competitive pricing.
Marketing and User Acquisition
Smart marketing ensures you're spending efficiently and acquiring the right users, not just more users.
Targeted Marketing Campaigns
- Segment users based on attributes like demographics, activity level, location, and preferences.
- Deliver personalized email campaigns, ads, or in-app promotions to specific user groups.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) & Lifetime Value (LTV) Analysis
- Calculate CAC by channel to identify which sources bring high-value users.
- Measure LTV to predict the long-term revenue potential of different segments.
Impact: Helps allocate marketing spend more effectively and boosts ROI on user acquisition strategies.
Trust and Safety
For two-sided marketplaces, trust is non-negotiable. Without it, transactions don’t happen.
Fraud Monitoring and Detection
- Track unusual behavior patterns (e.g., excessive cancellations, duplicate accounts, IP anomalies).
- Use predictive models to flag or block fraudulent activities in real time.
Feedback and Review Analysis
- Analyze reviews for sentiment and recurring complaints.
- Use insights to surface top-rated service providers or penalize low-quality service providers.
Impact: Builds a safer environment, improves platform reputation, and reduces disputes.
Case Studies on Data Analytics in 2-Sided Marketplaces
How Airbnb Leverages Data and Analytics
Airbnb is one of the most successful two-sided marketplaces in the world, connecting millions of guests with hosts offering unique places to stay. Behind the scenes, Airbnb relies heavily on data and analytics to optimize nearly every aspect of its marketplace platform, from user experience to trust and safety.
Personalization & User Experience
What they do:
- Airbnb uses user behavior analytics and machine learning models to recommend listings based on a user’s browsing history, trip context (e.g., solo or family travel), and preferences.
- Their search ranking algorithm takes into account over 100+ signals, including price, location, availability, user reviews, host responsiveness, and previous user behavior, all key elements of marketplace data insights.
Impact:
- Guests find suitable listings faster.
- Hosts see higher booking rates.
Example: If a user frequently books beachfront homes in summer, Airbnb starts surfacing similar listings proactively, even before a destination is typed in.
Dynamic Pricing with Smart Pricing
What they do:
- Airbnb’s Smart Pricing tool helps hosts automatically adjust their listing prices based on:
- Seasonality
- Local demand trends
- Listing popularity
- Local events (e.g., concerts, sports events)
- Similar listing pricing
This pricing strategy aligns with predictive analytics in marketplaces and contributes to dynamic pricing optimization.
Impact:
- Hosts maximize earnings while remaining competitive.
- Airbnb increases conversion rates and guest satisfaction.
Example: If a major event like the Super Bowl is happening nearby, Smart Pricing automatically raises prices on listings in that area.
Predictive Analytics for Growth & Retention
What they do:
- Airbnb predicts user churn and proactively re-engages users with targeted emails or discounts.
- It forecasts demand in different regions, helping the platform suggest where new hosts are needed.
Impact:
- Better marketing ROI and host acquisition.
- Balanced supply and demand across geographies using data-driven marketplace optimization
Example: If a user booked a ski cabin the previous winter, Airbnb may send curated options and discounts as the season approaches again.
Trust, Safety, and Fraud Prevention
What they do:
- Airbnb uses machine learning to score the risk of each booking before it happens.
- It evaluates dozens of signals, including.
- IP address inconsistencies
- Payment anomalies
- User account history
- Airbnb also uses NLP (Natural Language Processing) to analyze reviews for red flags (e.g., uncleanliness, suspicious behavior), showcasing effective use of real-time analytics for marketplaces.
Impact:
- Reduces incidents of fraud, fake listings, and risky bookings.
- Enhances user trust and platform credibility.
Example: If a new host creates multiple listings with the same photos or shows erratic behavior, Airbnb’s systems may suspend the account pending review.
Review System and Feedback Loops
What they do:
- Airbnb analyzes guest and host reviews using marketplace cohort analysis and sentiment analysis to assess:
- Listing quality
- Cleanliness
- Communication effectiveness
- These metrics contribute to superhost badges and visibility rankings, demonstrating how feedback loops and transaction analytics platforms improve decision-making.
Impact:
- Helps users make informed decisions.
- Encourages high-quality service from hosts.
Internal Tools & Infrastructure
Key Technologies:
- Airflow: for orchestrating data pipelines.
- Superset & Tableau: for internal dashboards and data visualization.
- Data Lakes & Warehouses: for unified data storage.
- ML Platforms: for building and deploying machine learning models (pricing, recommendations, fraud detection).
Key takeaways:
Airbnb is a textbook example of using data analytics marketplaces as a strategic asset. By embedding analytics into every layer of their business, from pricing to trust,they've built a scalable, trustworthy, and user-centric 2-sided marketplace platform.
How Uber Leverages Data and Analytics
Uber operates one of the most sophisticated two-sided marketplaces in the world, matching millions of riders with drivers in real-time. To deliver consistent, efficient, and scalable service, Uber deeply integrates data and analytics into every layer of its platform, from pricing and routing to safety and driver incentives.
Real-Time Matching & Dynamic Pricing (Surge Pricing)
What they do:
- Uber uses real-time data streams to match supply (drivers) and demand (riders) in milliseconds.
- When demand outpaces supply in a certain area, surge pricing is triggered to:
- Encourage more drivers to go to that area
- Balance rider demand with supply availability
How it works:
- Algorithms ingest real-time GPS, traffic, event, and demand data.
- Machine learning models predict short-term demand surges and adjust pricing dynamically.
Impact:
- Reduced wait times for riders
- Increased earnings for drivers during peak times
- Better geographic distribution of supply
Route Optimization & ETA Prediction
What they do:
- Uber optimizes routes using predictive analytics models that account for:
- Real-time traffic data
- Road closures
- Historical travel times
- Estimated Time of Arrival (ETA) models are continuously updated using rider and driver location data.
Tech used:
- Machine learning models such as XGBoost and neural networks for ETA prediction.
- Graph algorithms and real-time GPS data for route optimization.
Impact:
- More accurate ETAs increase rider satisfaction.
- Efficient routes lower fuel costs and increase driver efficiency.
Driver Incentive Programs & Marketplace Balancing
What they do:
- Uber analyzes driver behavior to offer tailored incentives (e.g., bonuses, guarantees).
- Predictive analytics in marketplaces helps forecast demand surges, allowing Uber to:
- Suggest hotspots to drivers.
- Offer incentives to shift behavior.
Example: If Uber predicts high demand in downtown from 5-7 PM, drivers nearby are offered surge multipliers or guaranteed trip bonuses.
Impact:
- Increases driver availability when and where needed.
- Balances the supply side of the marketplace without overstaffing.
Customer Segmentation & Personalization
What they do:
- Uber segments customers based on trip history, frequency, location, and spending behavior, driven by user behavior analytics.
- Data is used to:
- Personalize promotions (e.g., 20% off for frequent riders)
- Tailor app experiences based on travel patterns (e.g., suggesting "Work" or "Home")
Impact:
- Increases rider engagement and retention.
- Improves the effectiveness of promotions and marketing spend.
Trust, Safety & Fraud Prevention
What they do:
- Uber employs real-time analytics for marketplaces to detect:
- Fake accounts
- GPS spoofing
- Payment fraud
- NLP is used to analyze support tickets and incident reports.
- Safety features like “Share My Trip” and “RideCheck” use sensors and analytics to detect anomalies (e.g., sudden stops, long detours).
Impact:
- Reduced fraud and increased trust.
- Safer rider and driver experience.
Operational Forecasting and City Planning
What they do:
- Uber uses time-series forecasting to project demand patterns across cities.
- Data is used to:
- Plan city expansions
- Adjust pricing or incentives.
- Engage local regulators with anonymized trip data to help with urban planning
Impact:
- Strategic scaling into new regions
- Smarter regulatory compliance and better public relations
Key Takeaway:
Uber's success is rooted in a breathtakingly intelligent system of data and analytics. By turning raw data into actionable knowledge, Uber has built a platform designed for scalability, operational efficiency, trust, and satisfaction, setting the standard for data-driven decision-making in two-sided marketplaces.
Challenges and Considerations of Data and Analytics in 2-Sided Marketplaces
Although data and analytics can play a strong supporting role in decision-making in two-sided marketplaces, it is not problem-free. Ignoring and staying away from such issues could lead to biased decisions, user distrust, and inefficiencies in operations across the marketplace platform.
Common Pitfalls in Data Analytics for 2-Sided Marketplaces
Two-sided platforms are intricate ecosystems. Misreading marketplace analytics or measuring the wrong indicators can lead to second-best strategies and hinder data-driven marketplace optimization.
Key Challenges:
- Data Silos: Data silos occur when data is divided between different departments, operations, product, and marketing, for example, leading to different insights.
- Bias in Data: Using data from one side of the marketplace (e.g., consumers) can exclude the other (e.g., service providers).
- Overfitting: Predictive models trained on a narrow dataset may perform poorly in the real world.
- Vanity Metrics: Measuring superficial KPIs, such as signups, rather than more significant ones, such as activation or retention, is misleading.
Tip: Always validate model outputs using actual user behavior analytics and avoid relying on generic dashboards that ignore platform-specific patterns.
Importance of Data Privacy and Ethical Considerations
Two-sided marketplace platforms handle large volumes of personal and behavioral data, making data privacy and ethics non-negotiable.
Key Concerns:
- Data Ownership: Who owns the data, users, platform, or both? Lack of clarity can erode trust.
- Compliance Risks: Regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and others require strict consent, transparency, and data handling processes.
- Algorithmic Fairness: Biased recommendation or pricing algorithms may unintentionally disadvantage certain user segments, especially in transaction analytics platforms that rely on automated decisions.
Best Practices:
- Anonymize and encrypt user data wherever possible.
- Conduct regular audits of predictive analytics in marketplaces to ensure algorithmic fairness.
- Communicate how data is collected and used through updated privacy policies.
Balancing Data-Driven Decisions with Human Intuition
Valuable analytics often slip away, eclipsed by the relentless tide of automated decision-making, leaving the user experience wanting.
When to Step Back from the Data:
- Creative strategy: Branding and marketing have to win over the heart, not the head.
- Community building: Creation of the marketplace is predominantly driven by trust in the community, and demand and supply come second; human nature is more influential.
- Crisis management: Extremely volatile changes (PR crisis or market change) could favor humans over data.
Insight: Let data analytics for marketplace optimization inform but not override human judgment. The most resilient marketplace platforms blend machine precision with human sensitivity.
Final Thoughts on Data-Driven Growth in Two-Sided Marketplaces
The two-sided marketplace is also far more effective when it is data and analytics-led. It helps companies to see what people do and helps to find more people to grow. This is because of the clear, doable ideas that those who run the market can use to make the right calls that help all the people on both ends of the market, and keep them happy and coming back.
It’s a good time to review your current data strategy and consider implementing full-scale analytics solutions, be it for user behavior analytics, marketplace cohort analysis, or customer acquisition in marketplaces. Structured application of these tools unlocks your marketplace's full potential in an increasingly competitive digital economy.
Additional Resources For Data Analytics:
- Power BI – Microsoft’s business analytics platform.
- RapidMiner - A Powerful data analytics and AI platform that connects siloed data, unlocks hidden insights, and accelerates innovation.
- Tableau – A Visual analytics platform with strong storytelling tools.
- Excel / Google Sheets – still powerful for quick analysis
Books For Data Analytics:
1. Data Analytics Made Accessible by Dr. Anil Maheshwari
2. Data Science for Business




 June 25, 2025
June 25, 2025


