What Is Uber’s Business Model? How Uber Works? How Does Uber Make Money? What Is Uber’s Business Strategy? Why Is Uber so Successful?
These are some of the major questions any budding entrepreneur in the on-demand startup space would be curious about, before working on his/her own “Uber for X” business model.
And, rightly so.
Uber’s business model has turned out to be so successful and popular that it has fuelled a new startup economy, the “on-demand economy”.
Having a deeper understanding of Uber’s on-demand business model can play a pivotal role in modeling your own on-demand startup business idea.
As a leading on-demand startup technology development partner, we want to share this knowledge with you through this comprehensive blog post.
Uber Basics - Facts, Figures, Founders & Fundings
Before drilling down into “Uber’s business model” or “How Uber makes money?”, let us gain knowledge about some basics and interesting facts about Uber - from inception to being a multi-billion dollar startup.
Some Trivia
Did you know that Uber was initially called as UberCab?
Originally, the app only had the option to hail a black luxury car.
Founders - Garrett Camp, Oscar Salazar, Travis Kalanick
Founding Year - March 2009
Headquarters - San Francisco Bay Area, U.S.A
Legal Name - Uber Technologies Inc. (Crunchbase)
Total Funding - $24.2B (In 22 funding rounds as of Oct 2018, Crunchbase)
Major Investors - SoftBank Vision Fund, Tencent Holdings, Toyota Motor Corporation, and others.
Current Valuation - $120B (Source - Bloomberg)
Uber’s Business Model - How Uber Works?
Uber is no longer just the on-demand cab hailing service we used to know. It has dipped its toes into other territories as well - from Uber Eats (on-demand food delivery) to Uber Freight (on-demand trucking).
For the matter of simplicity, in this blog, we will focus on Uber’s core business of ridesharing - its business model and how it makes money?
To put it in simple words,
Uber works as a digital aggregator app platform, connecting passengers who need a ride from point A to point B with drivers that are willing to serve them.
“Passengers” generate the demand, “Drivers” supply the demand and “Uber” acts as the marketplace/facilitator to make this all happen seamlessly on a mobile platform.
Kool, right?
Through its model, Uber has been able to generate strong value propositions for both passengers and drivers to get onboard on its platform and create disruption in the taxi/cab industry.
If you're interested in Uber-like app development, understanding how Uber functions will be key to shaping the user experience and business structure of your app.
Uber’s Value Proposition for Passengers
- On-demand cab bookings (Convenient)
- Real-time tracking
- Accurate ETAs
- Cashless rides
- Lower wait time for a ride
- Upfront pricing
- Multiple ride options
Uber’s Value Propositions for Drivers
- Flexibility to drive on their own terms
- Better income
- Lower idle time to get new rides
- Training sessions
- Assistance in getting vehicle loans
- Better trip allocation
Uber’s Business Model Canvas - A Visual Snapshot
Click to Enlarge Image
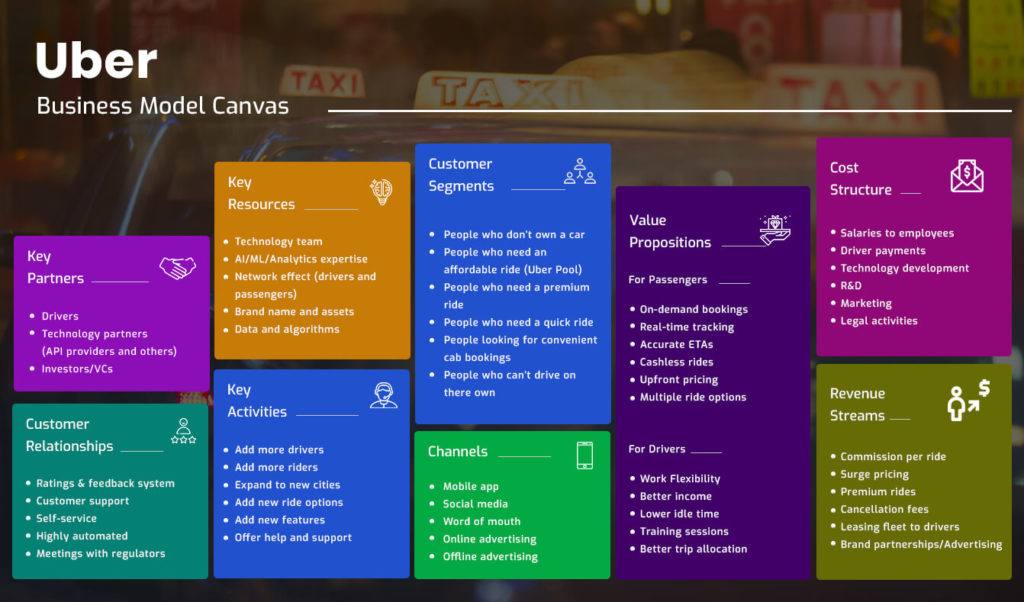
Digging Deep Into Uber’s Revenue Sources - How Uber Makes Money?
At a high level, Uber makes money by taking a cut on each ride (shared or individual) from the drivers. However, as we do a detailed analysis we will found that Uber’s revenue model is more complex than just trip commissions.
Trip Commissions
Uber provides the drivers on its platform (also called as partners) with a robust supply of ride requests to accept, fulfill, and make income. While making a booking, the passenger pays Uber for the ride through the app. Uber then transfers the payment to the partner’s account after taking some amount of commission for doing the job of a broker (digital broker if you want to say so).
The commission rates may vary from 15-30 % depending on the market.
Surge Pricing
Dynamic pricing/ surge pricing is a novel concept that has been popularized by Uber and being adopted in other verticals as well, such as food delivery.
Whenever there is a higher demand for cabs than what can be served at that moment (for example, at the airport after a flight lands), the fare goes up based on a surge price calculation algorithm.
Some drivers move to the surge region to earn extra (increases supply) and some passengers opt to wait to get a ride (reduces demand). This way Uber is able to manage the demand-supply mismatch situation better.
Drivers make more money, Uber makes more money and customers spend more money (but get urgent rides).
Premium Rides
Uber offers multiple ride options, from affordable hatchbacks to luxury sedans and SUVs. The profit margin for premium rides are much higher and helps Uber mint more money.
Cancellation Fee
If a passenger cancels a ride after a certain time-frame, say five minutes, he/she is charged a cancellation fee.
Leasing to Drivers
Uber runs a vehicle leasing program in many of its target countries to help new drivers get onboard faster. Drivers have to pay an upfront security deposit for the vehicle and payments are automatically deducted on a weekly basis from the driver’s earnings.
Brand Partnerships/Advertising
Uber is a very popular app with millions of active users. This makes it a good option for brands to do promotions. Its current app interface pushes a feed style layout for intuitive content consumption. Over the period, it may go on to become a strong revenue source by becoming a channel for sponsored content.
Expanding Rapidly With New Business Verticals
As mentioned earlier above, Uber is now much more than just a ridesharing company. It is leveraging it’s underlying technology for cab bookings, like, optimal driver allocation, to new use cases as well.
These new businesses that Uber is building side-by-side have tremendous potential to generate revenue and fuel Uber’s grand ambitions.
Uber Eats
Uber is betting big on on-demand food delivery and why not. It’s a logical step for Uber to tap into this enormous market as it aligns with its ridesharing business and helps it utilize its large fleet of drivers. Uber Eats was launched as a separate app in 2016 and is growing in popularity at a rapid rate.
Uber Freight
Uber Freight is basically Uber for trucks. Uber launched its own on-demand trucking app in 2017 with the core idea of seamlessly matching shippers with carriers. If Uber can execute on its strategy to become the freight matching platform of choice, the revenue opportunities are also big.
Key Takeaways for Budding Entrepreneurs From Uber’s Business Model Analysis
Uber got a lot right in its journey towards becoming a pioneer in the on-demand industry today. It has seen its fair share of challenges over the period and been able to maneuver through most of them successfully.
It is a great testament of a tech startup that achieved success with a novel business model and smart execution.
Interesting Read: How to Build an App Like Uber?
Tech entrepreneurs and startups can learn a lot from studying Uber’s business case study. We have tried to make the job easy by putting down a list of key takeaways/ tips from analyzing Uber’s massive success.
Let’s check them out below.
Build Solutions for Real-world Problems
This is somewhat obvious but still needs to be mentioned first. You as an entrepreneur should identify real problems and figure out how technology can be leveraged to solve it, just like Uber used mobile technology to transform on-demand transportation.
Keep Innovating
Uber doesn’t rest on its laurels of being the first prominent rideshare app. Its founders understood really well that the competition will grow over time and they can only stay ahead through continuous product iterations. They keep adding new features to their passenger and driver apps, invest in new technologies, and more.
For entrepreneurs interested in offering a different angle on ride-sharing, such as a bike ride booking app, continuous innovation will help you stay competitive in a growing market.
Shoot for Scalability
Building a scalable business model is critical if you are to sustain your startup in the long run. Uber has built its platform in such a way that it is easy for it to expand to new markets and serve multiple users simultaneously with confidence.
Keep Overhead Costs Low
Run a lean business model that doesn’t require large infrastructural investments. Also, for building a tech startup, a skilled workforce is very crucial. This also adds up to your cost overheads in terms of high salary payments. One effective way to stay lean during the initial stages of your product development is by partnering with a third-party technology development company to build the MVP and overtime do in-house hiring.
Wrapping Up!!
The proliferation of the on-demand industry owes a lot to Uber and rightfully so. Uber’s success in many ways started a chain reaction with hundreds of on-demand/ Uber for “X” startups been launched after that and hopefully many more to come.
Specifically, in the on-demand transportation and logistics industry, the effect has been profound. We hope that our analysis of Uber’s business model will become a useful resource for upcoming on-demand startups.

Disclaimer: The information mentioned in this blog is based on the author’s own understanding of Uber’s business model. The facts and figures have been obtained from online research with appropriate credits given wherever required. Please use the information at your own discretion with no liability on the author or the firm.



 January 2, 2019
January 2, 2019


