Healthcare has taken giant leaps from physical patient records to EHRs, telehealth, and healthcare apps. Online portals with seamless access to patient data have replaced registers with patient information in physical form.
While this seamless availability of protected health information (PHI) is beneficial for both patients and providers, it comes with a big roadblock – cybersecurity threats. As new technologies continue to revolutionize healthcare, several PHI security risks have also emerged.
Here’s a comprehensive understanding of how healthcare providers can mitigate PHI risks and vulnerabilities while offering the best-quality experience and care to their patients.
Peer-Driven Tactics to PHI Risk Discovery
The most prominent step in PHI risk management is to determine the risk. This includes identifying the data that PHI has access to and the impact it can create in case of a breach.
Nowadays, healthcare organizations leverage big data to store, share, and maintain large volumes of data. While this supports the delivery of proper and efficient care, it has its downsides. Service providers must deploy security measures and conduct HIPAA risk assessments to continually assess risk and safeguard both clinical and administrative data.
1 Determine PHI access
First, find out the protected health information accessibility. That’s the data required to protect. Determine which solutions are used to store and transmit data. Interview employees, review documentation, and analyze current projects to gain better insights.
2 Examine security measures
Once the data is identified that requires protection, identify the measures needed to achieve the desired level of security. Ensure that the employees are in line with the privacy and security requirements and the patient data management system offers adequate protection.
3 Understanding vulnerabilities and level of risk
No matter how robust the security infrastructure is, PHI breaches can happen. Therefore, it’s equally critical to realize organizational vulnerabilities and the possible exposure to potential cyberattacks. Determine the risk level for all exposures that can be encountered and the impact it could have. This will give a clear idea about where you stand as an organization from a security and privacy standpoint.
4 Finalize everything
The last step is to document everything and finalize it. Organizations and businesses can select a format that best suits their needs. Just ensure that the document is easy to comprehend and gives a clear idea about the risks and vulnerabilities associated with HIPAA-protected health information.
Increasing Role of Technology in Healthcare
Internet of Things and healthcare has bridged the gap between healthcare providers and patients. Patient-doctor interactions that were once limited to physical visits are now being conducted over telehealth apps.
While the Internet of Things applications in healthcare has opened the door for remote monitoring and seamless healthcare delivery, they have also put protected health information at risk. Most patient data is stored and available online, making it easier to access. Machine learning has emerged as an effective technology to tackle the cybersecurity risk associated with IoT devices. Whether the type of attack is known or unknown, ML-based models can protect against cybersecurity threats.
Vulnerabilities Placing PHI at Risk
Healthcare remains the most vulnerable sector to cyberattacks, with almost 80% of providers reporting at least two breaches. Hence, healthcare technology vendors need to readily assess PHI security risks. Let’s discuss some vulnerabilities that can put protected health information at risk.
1 Mobile devices and cloud
Mobile healthcare and telehealth apps have paved the way for portable communication between patients and providers. However, these devices lack the security of computer systems used in healthcare facilities. Using the cloud in portable communications further increases the risk of a potential breach, as users are responsible for compliance and data security.
2 Dissemination of data
The dissemination of data between health providers and third parties is a weak security link that causes numerous security breaches. Normally, these transfers occur over File Transfer Protocol (FTP) sites, lacking security and tracking capabilities. This makes it easier for cyber attackers to get access to the data being disseminated.
3 Outsourcing to third-party vendors
Many healthcare providers lack the technological capabilities essential to maintain PHI. They tend to outsource it to privately-owned third-party vendors that may not necessarily follow regulations like HIPAA.
4 Failure to assess risk
According to the HIPAA security rule, organizations must regularly perform risk assessments. Yet, many organizations avoid performing risk assessment and optimization, resulting in data breaches. It puts protected health information at risk and invites litigation and fines. Providers must implement and adhere to risk assessment policies, such as regularly reviewing data inventories and exploring weak links in security.
5 Lack of awareness and training
Organizations take around 280 days to identify and contain a breach. This delay boils down to a lack of awareness of system activity. When the infamous Anthem breach of 80 million records was analyzed, it was discovered that the breach began 11 months back. This delay is often a result of improper training.
Most organizations conduct General Security Awareness training, but it’s not enough. Workers need to receive training depending upon the technology implemented. Software Development Lifecycle and Secure Development Training are two training areas that healthcare technology providers should focus on.
Providers can alleviate these risks by readily identifying and neutralizing them. It’s essential to understand the scope of the PHI environment, including PHI entry, storage, and transmission. Familiarising with PHI environments, businesses can consider possibilities like:
- Potential vulnerabilities in the applications, systems, people, or processes.
- Types of threats that can exploit these vulnerabilities.
- Probability of each exploit.
Finally, assess your HIPAA risk level, along with the probability of threats and the impact they can have.
Real-Time Methods of Protecting PHI with Holistic (NIST-Compliant) Frameworks
Once the PHI vulnerabilities and their potential probability and impact are identified, organizations can implement methods to protect them. The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is a globally accepted suite of cybersecurity practices that enable PHI risk management. Let’s discuss the domains and how to use them for PHI protection.
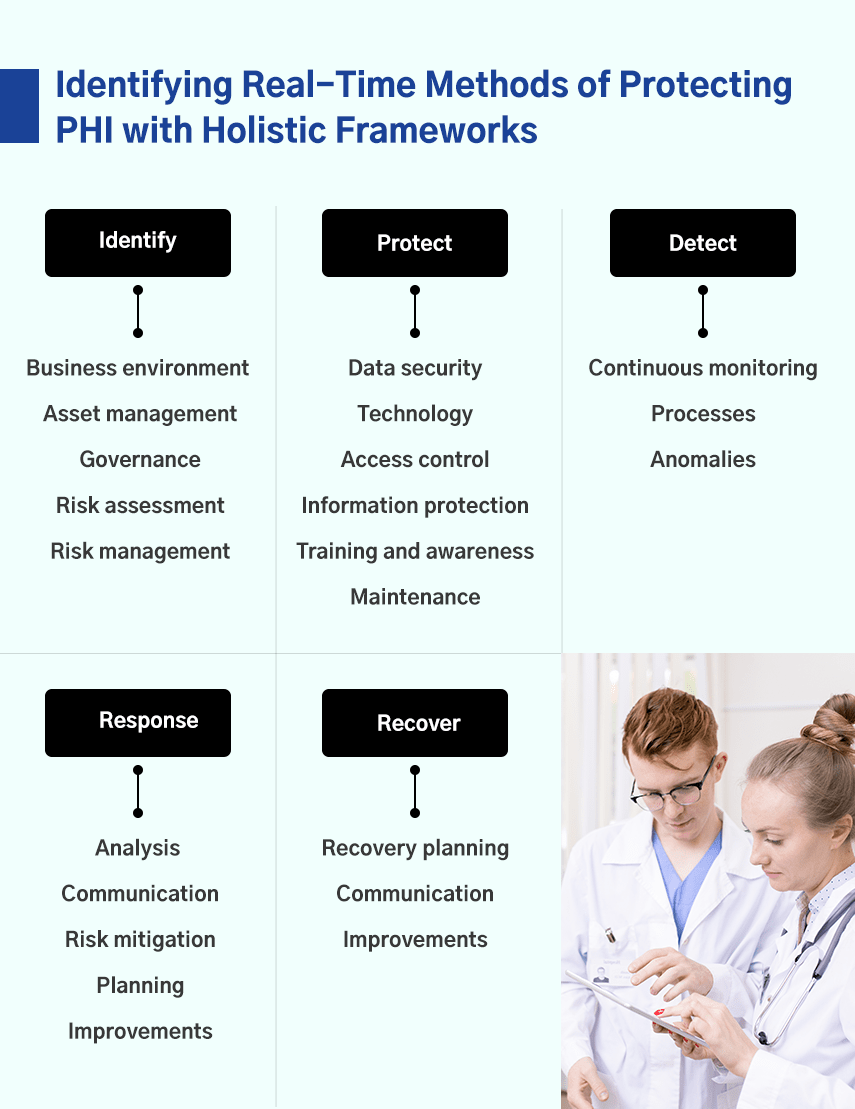
1 Identify
The first step is to fully understand the current PHI environment and the potential risks at different levels of the organization. This step includes rigorously identifying and evaluating assets, recognizing their role in protected health information, and the responsibilities of employees in managing those assets.
The key categories of the identification function are:
- Business environment: Processes, missions, activities, and objectives.
- Asset management: Devices, systems, applications, and facilities.
- Governance: People, leadership, management operations.
- Risk assessment: Potential threats and vulnerabilities.
- Risk management: Possible steps to increase risk tolerance and strengthen security.
2 Protect
The next step is to determine whether or not the current cybersecurity infrastructure offers sufficient protection against the identified risks. If not, what changes and additions are required to ensure appropriate protection against the threats.
The following are the key protection methods that organizations should implement:
- Data security: Safeguarding availability, confidentiality, and integrity of data.
- Protective technology: Implementation of a HIPAA breach risk assessment tool to achieve optimal information security.
- Access control: Limit access to information, networks, and assets.
- Information protection: Protect information and assets.
- Training and awareness: Provide training and cybersecurity awareness to employees.
- Maintenance: Repair IT system elements.
3 Detect
The detection aspect of the framework involves proactively identifying hospital cybersecurity events. As mentioned, it could take organizations a few months to identify a breach. Late identifications often result in bigger damages.
Here are three elements of detecting PHI cybersecurity events.
- Continuous monitoring: Continuously monitor cybersecurity events.
- Detection processes: Implement detection processes to detect events.
- Detecting anomalies: Detect all anomalies in real-time.
4 Respond
Cybersecurity attacks can happen even after ensuring proper preventive measures. In such cases, it’s essential to respond quickly and contain the adverse effects of the breach. An organization can take numerous steps to respond to a cyberattack, including:
- Analysis: Analyze the cause and potential impact of the breach.
- Communication: Communicate the incident with internal and external stakeholders.
- Risk mitigation: Neutralize the effects of the breach.
- Response planning: Plan a response to the breach.
- Improvements: Identify shortcomings and make improvements.
5 Recover
The final step in the NIST Cybersecurity Framework is to revive impaired services and ensure that everything starts working as usual. Organizations can take the following steps to recover their operations.
- Recovery planning: Organize and prioritize recovery procedures.
- Communication: Coordinate communication with stakeholders.
- Improvements: Improve your recovery strategy.
PHI Risk Mitigation
With PHI risk on the rise, healthcare IT providers are incorporating risk mitigation processes. Organizations can take numerous steps to strengthen their PHI risk management strategies for mitigation efforts. Including:
1 Discovery and Classification records of the organizations
If organizations have an influx of data incoming, it’s essential to identify and classify data as PHI and Personally Identifiable Information (PII). This way, organizations can prioritize the confidentiality and integrity of at-risk data. Also, assess the impact on your organization if a PII or PHI breach occurs.
2 Implement policies and access controls
The majority of data breaches happen due to an internal mistake. Often, employees lack security awareness, which increases the cybersecurity risk. To avoid this, companies can implement data and access controls to restrict access to critical information. Additionally, assessing associates with a data security questionnaire can test their knowledge.
3 Monitor continuously
It’s essential to continuously monitor the effectiveness of security policies and frameworks. At any given time, businesses must have sufficient visibility of the potential risks that unsecured PHI is exposed to and what can be done to alleviate those risks.
4 Limit employees with PHI access
HIPAA instructs organizations to limit the flow of confidential information within an organization to avoid and mitigate PHI risk. Organizations can do this by reducing the number of associates with access to PHI data. They can form a specific team of employees who can access PHI information to avoid potential risks.
5 Use the right technology and tools
Healthcare technology has come a long way, and it can help you implement effective PHI risk management solutions to mitigate PHI risk. These tools automate tasks like continuous monitoring and allow you to manage multiple security frameworks within a single platform.

Innovation in Machine Learning and Telemetry
Machine Learning has already been established as a world-changing technology, but the pandemic took its usage to a whole new dimension. From facilitating research & development to streamlining organizational operations, ML has changed the way organizations are conducting business.
ML has had a substantial impact on the healthcare industry as well. 50% of hospitals already have an Artificial Intelligence (AI) framework, with the remaining respondents willing to adopt one within two years.
Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Transforming the Practice of Medicine
One of the major applications of ML in healthcare is to leverage telemetry data by gaining hidden insights. As big data in healthcare has become the new normal, healthcare organizations generate massive amounts of complex telemetry data. However, not many providers have the right tools and technologies to turn this raw telemetry data into useful and actionable insights.
These tools provide various data analysis benefits, including:
- In-depth visibility into the networks required for monitoring.
- Clear insights into the performance of business networks.
- Predictive Analytics for forecasting future trends and behaviors.
- Enhanced network security.
Final thoughts,
The right quantity of data is not a problem for most organizations. The right quality of data is, however, a challenge. By implementing and training ML models, including flow, congestion, and drop reports, providers can enhance network security, identify correlations, and anticipate future outcomes.
While the opportunities telehealth, IoT, and big data offer for healthcare are substantial, they result in several obstacles that providers need to address. Healthcare-based companies like Mobisoft Infotech can help mitigate PHI risks and other cybersecurity breaches.




 August 10, 2021
August 10, 2021


