The online shopping platform is no longer just a choice; it's a driving force in global commerce. Entrepreneurship in the ecommerce industry and running an ecommerce business come with unprecedented opportunities and evolving challenges. International ecommerce sales will keep growing strongly, reaching pandemic highs and ready to shatter past records. Customers are more comfortable than ever making purchases online, driven by convenience, accessibility, and the increasing sophistication of digital experiences.
But the market is more competitive. Rising customer demands, costlier ecommerce marketing due to privacy shifts, possible supply chain issues, and the requirement for technological agility (particularly with AI) mean that simply having a product and a website is no longer enough. It takes a deliberate strategy not only for launch but for long-term growth in your online business.
This comprehensive guide is your roadmap. We'll walk you through every step essential to validate your original concept to scale your business to become profitable in the long term. We'll discuss market entry strategies and explore the strategies required to create a strong, future-proof e-commerce business.
If you're an entrepreneur looking to start a new business or restart an existing one, this guide gives you the information and step-by-step instructions you need to succeed using the best ecommerce platform and foundational ecommerce website principles.
Phase 1: Establishing the Foundation – Preparation for Success
Before you even get as far as contemplating ecommerce website design or ecommerce marketing strategies, a solid foundation is required. Rushing through this process is a common error that can ruin even the best of ideas.
Step 1: Idea Generation and Niche Selection
Every business starts as a concept. But not every concept turns into a successful online business. The appropriate niche is what makes the difference.
Identify Problems & Passions
What problems can you solve for consumers? What are you passionate about? The intersection of market opportunity and personal passion seems to result in more resilient businesses.
Analyze Trends (Sensitively)
Use tools like Google Trends to gauge consumer demand. Project ahead to trends like sustainability (re-commerce is picking up steam), personalization, health & wellness, and niche passions. But watch out for fleeting fads. Focus on trends with longevity and potential in the ecommerce business landscape.
Niche Down
Broad markets are often saturated. Specializing in a particular sub-segment (e.g., "sustainable pet toys for big dogs" rather than merely "pet toys") enables you to serve a dedicated audience, establish authority, and possibly experience less direct competition in the ecommerce platform space.
Profitability Potential
Research potential product margins, market size, and level of competition. Is the niche large enough to support a business yet specialized enough to differentiate and scale using a suitable ecommerce website builder?
Step 2: Market Research and Validation
After you have a niche concept, test it. Assumptions are bad in business, especially in the ecommerce marketing realm.
Define Your Target Audience
Create detailed buyer personas. Who are your best customers? What are they demographically, psychographically, their pain points, what they do online, and where do they congregate online (social media sites, forums)? Understanding this in depth dictates everything from product development to ecommerce customer acquisition efforts.
Competitor Analysis
Identify your primary competitors. Strengths, weaknesses, prices, ecommerce marketing, customer feedback, and site experience (SWOT analysis). One example is The Journey of a Fashion Retailer’s Online Transformation to Reach a Global Audience, where a deep market insight led to a global digital expansion.
Market Validation Methods
- Surveys & Interviews: Ask actual potential customers directly about their needs, preferences, and willingness to pay.
- Landing Page Test: Build a basic landing page explaining your product/concept and gather email sign-ups to measure interest.
- Pre-orders: Provide limited production of your product for pre-order to gauge demand before investing heavily.
- Keyword Research: Utilize SEO tools (such as Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, Ahrefs) to see if individuals are actually searching for products such as yours using terms like what is e-commerce, how to start an online store, or ecommerce website templates.
Step 3: Choosing Your Business Model
How will you operate? There are several models, each having pros and cons.
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C)
You produce/source and sell your own branded products directly to consumers through your ecommerce website. Provides complete control of brand and customer experience but with inventory management and entire initial investment.
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
Sale of products directly to end consumers (typically aligns with D2C).
Business-to-Business (B2B)
Simple sales of goods or services to businesses. B2B customers increasingly expect modern, B2C-style ecommerce website design.
Dropshipping
You market and sell products but have a third-party supplier who holds inventory and ships. Lower initial expense and risk but lower shipping, quality, and brand control. Margins could be lower.
Print-on-Demand (POD)
Like dropshipping, but from custom printed pieces (t-shirt, mug, etc.). Items are printed as ordered and shipped. Ideal for designers, minimizes risk in inventory.
Subscription Commerce
Customers subscribe to products or services for a recurring fee (e.g., specialty boxes, software subscription, replenishables). Great for recurring revenue and ecommerce customer retention, but necessitates constant value delivery.
Marketplace Selling
Selling through established marketplaces like Amazon, Etsy, eBay, or potentially new players like TikTok Shop (though its long-term sustainability is doubtful). Exposes you to a large audience but with charges, less control over your brand, and direct platform competition. Look at platforms that are strategic to your location or niche (like Alibaba in China). Consider using the best ecommerce platforms for small businesses if you're just starting out.
Private Labeling
Purchasing generic items from a manufacturer and reselling them under your label. Allows for brand development without a manufacturing facility.
Affiliate marketing
Promoting other companies' products and receiving a sales commission for sales generated through your referral links. Smaller barrier to entry, but dependent on traffic generation and partner relationships.
Your choice relies on capital, risk tolerance, product type, and long-term objectives. You can even blend models depending on your chosen ecommerce platform. At this stage, exploring professional Ecommerce Development Services helps ensure your business model aligns with technical feasibility.
Step 4: Creating an Effective Business Plan
Even for a small ecommerce website, a business plan is required. It forces you to think long and hard about every aspect of your online business and serves as a guide.
Key areas to include:
- Executive Summary: Short description of your company
- Company Description: Mission, vision, values, legal structure
- Market Analysis: Target market, market size, competition
- Products or Services: What you're selling, unique selling proposition (USP)
- Marketing and Sales Plan: How you will sell to and market customers
- Operations Plan: Sourcing, inventory, fulfillment, technology
- Management Team: Your experience (or plans to hire)
- Financial Plan: Initial costs, funding sources, projected revenues, profitability
Step 5: Legal Structure and Registration
Getting the legal bits right in the beginning avoids huge headaches down the road when starting an online business.
Choose a Business Structure
Sole Proprietorship, Partnership, Limited Liability Company (LLC), Corporation (S-Corp or C-Corp). Each has different implications for liability, tax, and management. LLC is most popular among small businesses since it offers liability protection. Consult lawyers before formalizing your ecommerce business or launching a new ecommerce platform.
Register Your Business Name
Register your chosen name (check for availability first). You might need a "Doing Business As" (DBA) registration if you're operating under a name that is not your legal name. This is crucial for building your ecommerce website identity.
Obtain Licenses and Permits
These vary by location (country, state, city) and industry. Research federal, state, and local regulations. These may involve business operating permits, tax identification numbers (e.g., an EIN in the US), and industry-specific licenses for running your e-commerce business.
Know Tax Obligations
Sales tax (if you're in some specific location), income tax, maybe employment taxes if you have employees. Know sales laws online and how they apply to your ecommerce website builder or custom ecommerce website design services.
Main Website Policies
- Privacy Policy: Required if you're gathering personal information (which most ecommerce sites do in practice).
- Terms and Conditions (Terms of Service): Creates terms of use for your website, payment terms, disclaimers, limitation of liability, intellectual property rights.
- Return and Refund Policy: Define your policy. This is a necessity for building customer trust and is mandated by consumer protection legislation. Returns should be simple.
- Shipping Policy: Develop shipping processes, charges, delivery time, and international shipping information.
- Cookie Policy: Required under GDPR/PECR. Explain how you employ cookies and obtain consent.
- Intellectual Property (IP): Register your brand name and logo as trademarks. Register original content, images, and product designs on your website under copyright.
- Payment Card Industry (PCI) Compliance: Since you're accepting credit card payments, you'll need to adhere to PCI DSS standards to secure cardholder data. Any good payment gateways do that.
Step 6: Branding: Creating Your Identity
Your brand is more than a logo. It's what the customers think of your company, especially in online shopping experiences.
- Define Your Brand: Mission, values, personality, unique selling proposition (USP). What is it about? Who are you attempting to connect with?
- Select a catchy business name: Verify availability (domain name, social media handles, trademark).
- Design Visual Identity: Logo, color palette, font, imagery aesthetic. Apply it consistently everywhere.
- Brand Voice: How do you connect with your audience?(e.g., professional, playful, empathetic)
Phase 2: Building Your Online Front Door
Having planned, we can now build the ecommerce website where the transactions are taking place.
Step 7: Selecting the Appropriate eCommerce Platform
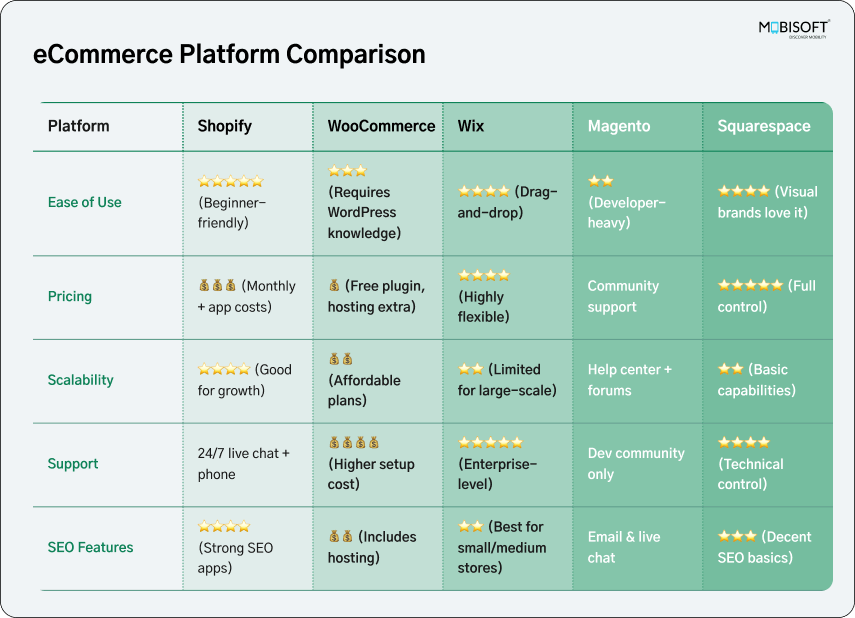
This is a high-level technical decision that influences functionality, scalability, cost, and usability when choosing the best ecommerce platform for your brand.
Hosted Platforms (SaaS - Software as a Service)
- Shopify: Frequently voted best overall platform, particularly for new and small businesses. Simple to use, massive app store for add-ons, good marketing integrations, scalable plans. Can charge transaction fees if not using Shopify Payments, and app fees can accumulate.
- BigCommerce: Solid platform with a high level of native functionality (less app needs), solid SEO functionality, no transaction fees on lower-end plans. Potential for a steeper learning curve than Shopify, possibly more costly themes. Ideal for larger companies that need customizations.
- Squarespace: Renowned for beautiful templates and ease of use (drag-and-drop editor). Suitable for visual brands and less complicated stores. ECommerce functionality is integrated but could be less advanced than Shopify/BigCommerce for more complicated needs. The SEO functionality is sufficient but maybe less effective.
- Wix: Another extremely popular site builder with great eCommerce functionality. Provides AI-based setup, point-of-sale integration, and decent design flexibility. Good for creating a complete site where the store is only one part of the site.
- Sellfy: Excellent for quickly building basic stores, particularly for digital products, subscriptions, and print-on-demand. Very simple to use.
- Square Online: Great option if you also have offline (brick and mortar) sales, with online and offline sales/inventory nicely integrated. Start with a free plan.
- Ecwid by Lightspeed: Provides a free starter plan and can be easily embedded into an existing site.
Open-Source Platforms
- WooCommerce (WordPress Plugin): Very flexible and customizable, leverages WordPress power. You own and control it. More technical expertise required to install and use (security, hosting, updates). Large plugin and theme community.
- Magento Open Source (Adobe Commerce): Extremely powerful and scalable, best suited for large companies. Requires a great deal of technical expertise and resources. For those seeking tailored functionality, Custom Ecommerce Development is often a necessary path.
- PrestaShop, OpenCart: Other open-source options with thriving communities.
Things to Keep in Mind:
- Budget (monthly subscription, transaction fees, app fees. Most offer free trials.)
- Simplicity vs. level of customization required
- Scalability
- Required features
- Marketing tools
- SEO
- Specific product types
- Technical skills
- Integration capabilities.
Step 8: User Experience (UX) and Website Design
Your site is your store. It should be functional, appealing, and simple to use. Prioritize ecommerce conversion rate optimization.
- Mobile-First Design: Google uses mobile-first indexing. Ensure your website is completely responsive and provides an excellent experience on tablet and smartphone devices.
- Simple Navigation: Offer users simple navigation to products (well-structured categories, search box, filtering).
- High-Quality Product Images & Videos: Use clean, professional images of different angles. Product demo videos can have a dramatic impact on conversions.
- Great Product Descriptions: Highlight specifications, benefits. Be convincing, bring in keywords naturally, and perhaps use AI tools to help write descriptions (but edit for originality). Highlight customer pain points.
- Clear Calls-to-Action (CTAs): Buttons such as “Add to Cart,” “Buy Now,” “Learn More” should be clear and visible. Learn more in our guide to 9 Must-Have eCommerce Features for creating a successful store experience.
- Fast Load Speed: Slow sites lose customers and rank poorly. Optimize images, keep code clean, choose good hosting.
- Streamlined Checkout Process: Fewer steps, offer guest checkout, clearly state costs (shipping, taxes) upfront. Abandoned carts are a huge issue; make checkout frictionless.
- Trust Indicators: Display security badges, customer reviews/testimonials, open contact information.
- Accessibility: Designing for people with disabilities (WCAG guidelines). Brands aiming for a wide-reaching user experience often leverage industry-focused Retail & Ecommerce Solutions.

Step 9: Product Sourcing and Inventory Management
How will you get your products?
- Manufacturing: Produce your own proprietary items. High control, potentially greater margins, but with high investment and lead times.
- Wholesaling: Buy large quantities of products from producers or wholesalers at a reduced rate and resell them. Engage in inventory storage and handling.
- Dropshipping/POD: Supplier ships and maintains inventory. Less risk, but less control.
- Crafting/Handmade: Making them yourself. Scalability can be a problem. Solutions like Product Configurators for Fashion Brands are helping creators balance personalization with scale.
- InventoryManagement:
- Track inventory levels closely to avoid overselling or stockout.
- Implement inventory control software (most platforms have an in-built application or integrations).
- Consider stock models like Just-in-Time (JIT) or carrying safety stock for anticipated demand.
Step 10: Payment and Delivery Terms
Payment Gateways
Select secure providers to handle online payments (Shopify Payments, Stripe, PayPal, Square, Amazon Pay). Make sure to be PCI compliant. Provide several payment options favored by your target audience.
Shipping Strategy
Use branded, sustainable packaging aligned with ecommerce marketing strategies.
- Fees: Choose free shipping (may increase conversions but erodes margins), flat rate shipping, or calculated shipping in real time.
- Carriers: Utilize reliable carriers (e.g., FedEx, UPS, USPS, DHL). Consider regional/international carriers.
- Fulfillment: Will you ship and pack orders yourself (in-house) or through a third-party logistics (3PL) company? 3PLs handle storage, packing, and shipping for you, saving you time but costing you money.
- Packaging: Consider branding and sustainability. Minimalist, recyclable packaging is increasingly important to consumers.
- Tracking: Give customers real-time order tracking details.
- Returns (Reverse Logistics): Have a simple, straightforward returns policy. This is for repeat business and customer satisfaction. Factor in reverse logistics costs.
Phase 3: Market Entry: Launching Your Business
The planning and construction are complete. It's time to launch.
Step 11: Generation of Pre-Launch Buzz
Don't just turn the switch. Build suspense.
- Coming Soon Landing Page: Collect email addresses of potential customers who are interested.
- Social Media Teasers: Share sneak peeks of products, behind-the-scenes content.
- Early Bird Offers: Offer exclusive discounts/offers to early subscribers/buyers.
- Influencer Outreach: Contact relevant influencers for potential early reviews or mentions.
Step 12: The Launch Strategy
- Soft Launch vs. Hard Launch: Do a soft launch (to a subset of the customer base) to pilot systems and gather feedback before a public launch.
- Coordinate Marketing Efforts: Coordinate email campaigns, social media announcements, and any launch day paid advertising.
- Monitor Performance: Monitor website traffic, server performance, and first sales closely. Be prepared to debug.
Step 13: Early Marketing and Customer Acquisition
You need to drive traffic to your new store. Focus on 1-2 best channels first rather than trying to do it all.
Paid Advertising (Warily):
- Social Media Ads (Meta, TikTok, Pinterest): Demographic, interest, behavior-based targeting. Costs are going up, so efficiency is key.
- Search Engine Marketing (SEM - Google Ads): Reach active users searching for your products.
Social Media Marketing: Create a presence on sites where your target audience congregates (e.g., Instagram, TikTok if you're selling to Gen Z, Facebook). Engage and grow the community, but don't sell only. Research social commerce features.
Influencer Marketing: Collaborate with relevant influencers to tap into their following.
Content Marketing (Begin Early): Begin creating informative blog posts, guides, or videos on your subject to generate organic traffic in the long run.
Email Marketing: Nurture pre-launch leads collected. Offer a welcome discount.
Key Tip: Don't anticipate profitability in year one. Concentrate on learning, getting first customers, and collecting data.
Phase 4: Day-to-Day Operations and Optimization
Launch is merely the start. Running and optimizing your business is a continuous task.
Step 14: Customer Service Excellence

Great customer service is one of the strongest differentiators and loyalty drivers. For example, in this Digital Commerce for Retail Chain: A Case Study, streamlined support made a tangible impact on customer retention.
- Multi-Channel: Support via email, live chat, phone, social media.
- Prompt Responses: Aim for immediate and helpful responses. Simple questions can be responded to by AI chatbots 24/7.
- Empathy and Problem Solving: Train support staff (or yourself) to deal with complaints professionally and to make the negative experience a positive one.
- Proactive Communication: Notify customers of order status, delays, etc.
Step 15: Fulfillment and Logistics
Effective fulfillment is important to ensure customer satisfaction.
- Accuracy: Make sure the right things are sent and packaged.
- Speed: Deliver within or earlier than negotiated timeframes. Buyers want speedy delivery.
- Communication: Provide regular tracking updates.
- Returns Management: Manage returns and refunds efficiently based on your policy.
Step 16: Analytics and Performance Monitoring
You can't measure what you can't have. Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) regularly.
- Website Traffic: Sources (organic, paid, social, referral), volume, user behavior.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of visitors who buy.
- Average Order Value (AOV): Average value spent on an order.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The cost of obtaining a new customer.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Total revenue expected from a single customer over time.
- Cart Abandonment Rate: Members adding products to cart but not finalizing the purchase.
- Impressions & Visibility: Especially with the growth of zero-click searches. Track visibility in search results, not clicks.
- Tools: Google Analytics 4 (GA4), platform-specific dashboards (Shopify Analytics, etc.), SEO tools. Make your decisions data-driven.
Phase 5: Attaining Sustainable Growth
Once your business is established, and stable, focus on long-term, sustainable expansion. This is not just a question of revenue growth; it's about building a good, profitable, and perhaps meaningful business.
Step 17: Advanced Marketing Strategies
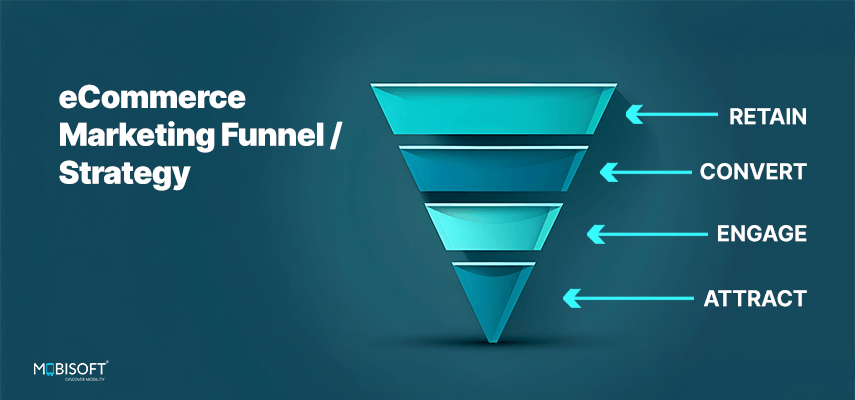
Transition from early acquisition plans.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
A sustained traffic plan for organic traffic.
- Keyword Research: Employ appropriate keywords, i.e., long-tail, natural keywords (voice search).
- On-Page SEO: Optimize product names, descriptions, URLs, image alt text, internal linking.
- Technical SEO: Mobile-friendliness, site speed, site structure (sitemaps), structured data (schema markup) for rich snippets. Feed-based tech SEO gaining more impact.
- Content Marketing: Create high-quality, relevant content (blog posts, guides, videos) that attracts links and establishes authority. Match user search intent.
- Link Building: Acquire high-quality backlinks from authoritative sites to establish credibility. PR and brand reputation are becoming more crucial for visibility in AI-based search.
- Voice Search Optimization: Use natural language, long-tail keywords, and format content for short answers.
- Zero-Click Optimization: Optimize to show up on featured snippet results, "People Also Ask" boxes, and other SERP features because users are getting answers on Google itself. Optimize to show up on impressions and brand views.
Content Marketing Deep Dive
Develop a content strategy that aligns to customer journey phases. Use pillar pages (like this one!) and topic clusters. Repurpose content across channels (blog, video, social).
Email Marketing Automation
Segment your list. Build automated sequences: welcome series, cart abandonment recovery, post-purchase follow-ups, re-engagement campaigns. Personalize emails on the basis of purchase history and behavior.
Social Media Engagement & Community
Build real relationships. Respond/comment on messages. Interact with user-generated content (UGC). Examine live shopping and social commerce integrations. Target content by platform (e.g., short-form video on TikTok).
Customer Retention & Loyalty Programs
Keeping the existing customers is cheaper than finding new ones. Utilize loyalty programs, offer special offers, personalized recommendations, and enhanced post-purchase support. Focus on CLTV expansion.
Referral Marketing
Encourage satisfied customers to refer friends in exchange for rewards. Word-of-mouth is powerful.
Step 18: New Channels and Markets
- Omnichannel Selling: Blend online and offline interactions (if applicable, e.g., purchase online, in-store pickup). Develop a cohesive brand experience across all touchpoints.
- Marketplace Expansion: Strategically expand to relevant marketplaces (Amazon, eBay, niche sites) to reach new customers. Be aware of the pros and cons.
- Cross-Border eCommerce: Go global. Requires research on customs, regulation, shipping, cost of shipping, payment options, and localization (language, currency). Can be enabled through collaboration with logistics experts.
- New Sales Channels: Investigate advertising in new channels such as mobile games or streaming television.
Step 19: Leveraging Technology for Efficiency and Experiences
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- Personalization: AI-driven product recommendations, personalized marketing messages.
- Customer Support: Immediate support through AI chatbots.
- Operations: AI for demand forecasting, inventory optimization, fraud detection.
- Content Generation: Assisting with product descriptions, marketing copy (always requires human oversight).
- Automation: Automate marketing repetitive tasks (email campaigns), customer service tasks (ticket routing), and fulfillment. Leveraging Ecommerce App Development solutions can streamline these workflows even further for mobile-first consumers.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Enables shoppers to see things in context (furniture) or virtually attempt to wear or use them (clothing, makeup). Is decreasing return numbers and increasing customer confidence. Growing use of AR considerably.
Step 20: Sustainable Practices
Sustainability is no longer a niche concern; it's an emerging expectation, especially with millennials. Combining sustainability can be lucrative and ethical.
- Environmentally Friendly Products: Source or make products from sustainable materials or by ethical processes.
- Sustainable Packaging: Utilize recycled, recyclable, biodegradable, or minimal packaging. Reduce waste.
- Carbon-Neutral Shipping: Align with carriers that have greener options or carbon offsetting. Offer green shipping as an option.
- Reduce Waste: Optimize inventory to prevent surplus. Explore re-commerce or take-back programs for reverse items.
- Transparency: Report your sustainability efforts clearly to your customers. Develop site-specific web page content about your efforts.
Step 21: Finance and Scaling
Track Cash Flow: Key to survival and growth.
- Pricing Strategy: Regularly review pricing on the basis of costs, competition, perceived value, and profitability targets.
- Budgeting & Forecasting: Accurately budget costs and forecast revenues.
- Profitability Analysis: Look at what products/channels are most profitable.
- Financing: Have financing alternatives (investment, loan) available when and if there is substantial growth, but maintain a healthy plan for ROI.
Step 22: Creating a Team
You can't do it all yourself forever.
- Identify Needs: Identify where and when you require assistance (customer service, marketing, fulfillment, technical).
- Outsource vs. Hire: Start with outsourcing certain tasks to freelancers or agencies. Hire staff for important, routine tasks when you scale up.
- Culture: Develop a robust corporate culture aligned with your brand values.
Future-Proofing Your eCommerce Business
The eCommerce environment is ever-changing. Be flexible. Keep an eye on these trends: Top E-commerce Trends 2025 gives a forward-looking take on what’s next.
- Hyper-Personalization: AI will enable even more precise personalization at every stage of the customer journey.
- Continued Expansion of Social & Live Commerce: Social buying within the social media platforms and via live streams will gain more mainstream acceptance.
- Voice Commerce: Voice search queries on smart speakers will become increasingly important.
- Data Privacy & Security: Regulation will continue to get more stringent. It is not a choice to make data practices transparent and secure.
- Sustainability as Standard: Green practices will be table stakes and not differentiators.
- AI Evolution: AI will become more and more integrated into all aspects of eCommerce, from discovery to post-purchase.
- Omnichannel Fluidity: Smooth blending of physical and digital interactions will continue.
- Headless Commerce: Decoupling front-end presentation and back-end operations to allow more flexibility (more applicable to big, complex companies).
Conclusion: Your eCommerce Journey Begins Now
Building and running a successful eCommerce business is a marathon. It takes planning, calculated risk-taking, good insight into your customers, and a willingness to keep learning and adapting.
From verifying your niche and navigating legal compliance to mastering digital marketing and adopting green practices, it's a tricky path but an incredibly rewarding one. The major pillars are: a good base in planning and research, customer-oriented strategy with experience and trust at the forefront, smartly utilizing technology (particularly AI and automation), and adopting sustainable long-term growth tactics versus short-term quick fixes.
The opportunities in the ever-expanding digital marketplace are endless. With the steps as described in this guide, keeping up with new trends, and being receptive to change in your approach, you can build an eCommerce business that will be profitable for
Are you ready to start? Plan today.





 April 22, 2025
April 22, 2025


