Historical Context
Before the Internet became common, most of the web applications were written for a relatively small group of users. For example, sales department of a company, HR department of a company, etc. With such business applications, the maximum number of users using the application was limited to all employees of the company for which the application was being deployed. In such case, a single powerful server could fulfill the requirement of that one company. With the advent of the Internet, now companies could reach hundreds of millions of users across the world. For really popular applications, this meant that at one time millions of users could be active on your web application. With such kind of traffic, one single server, no matter how powerful, will not be able to serve all of the active users. So software architects tried to handle this problem with clustering web application servers behind load balancers. Shared Nothing Architecture is a set of guidelines which allow you to design web applications that can scale to millions of users.Vertical Scaling vs. Horizontal Scaling
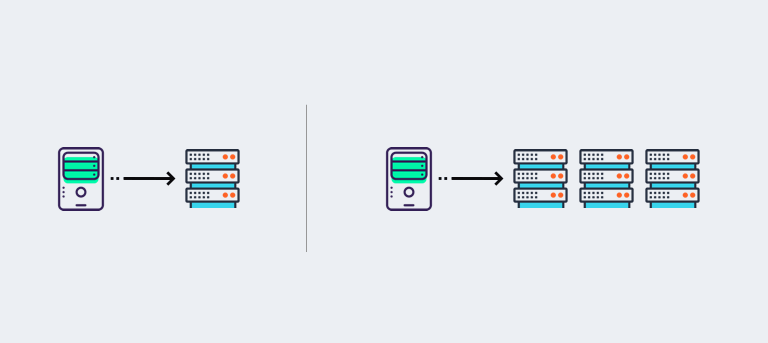
- Vertical ScalingVertical Scaling is a technique in which you increase the throughput of your deployment by increasing the physical hardware on a single machine. For example, you have a server with 2 CPU cores and 4GB RAM. Once you find that this server is reaching to its capacity, you can replace the server with a bigger machine, let's say, with 4 CPU Cores and 8 GB RAM. However, there is a limit to such kind of scaling. Let's say you have a machine with the highest possible configuration. If that machine can’t handle the load you have, then this solution can’t work.
- Horizontal ScalingIn Horizontal Scaling, you increase the throughput by increasing the number of servers. If the application is architected in a right way, there is no limit to what your application can scale up to. This technique, according to Google is by far the most popular in modern times. To support horizontal scaling you need to implement Shared Nothing Architecture, as all the big social applications use it.
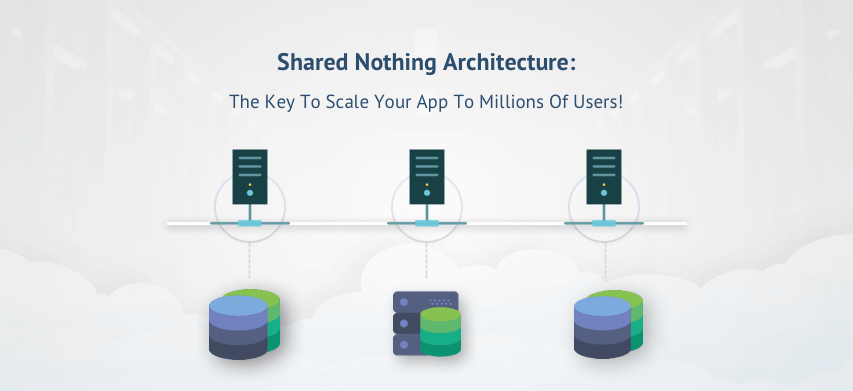
Shared Nothing Architecture
According to the definition by Wikipedia, “A shared-nothing architecture (SN) is a distributed computing architecture in which each node is independent and self-sufficient, and there is no single point of contention across the system. More specifically, none of the nodes share memory or disk storage.”Simplified Web Application Architecture
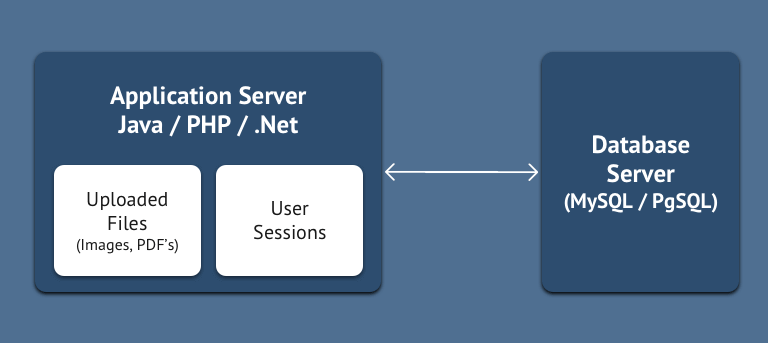 Typically, web applications have an application server, such as Tomcat, Apache + Mod_PHP, etc., along with a DB (database) server. The same physical machine which has application server is also used to store the uploaded files. Most of the application servers come with built-in session handling. These sessions are generally stored in the memory of the application server and optionally are persisted on the same server as files. The problem arises with this approach when you need more than one application server. Since the physical machine used for the second application server is different from that of the first one, they don't have access to each other's filesystem. So this architecture can't scale horizontally.
Typically, web applications have an application server, such as Tomcat, Apache + Mod_PHP, etc., along with a DB (database) server. The same physical machine which has application server is also used to store the uploaded files. Most of the application servers come with built-in session handling. These sessions are generally stored in the memory of the application server and optionally are persisted on the same server as files. The problem arises with this approach when you need more than one application server. Since the physical machine used for the second application server is different from that of the first one, they don't have access to each other's filesystem. So this architecture can't scale horizontally.
Shared Nothing at Application Layer
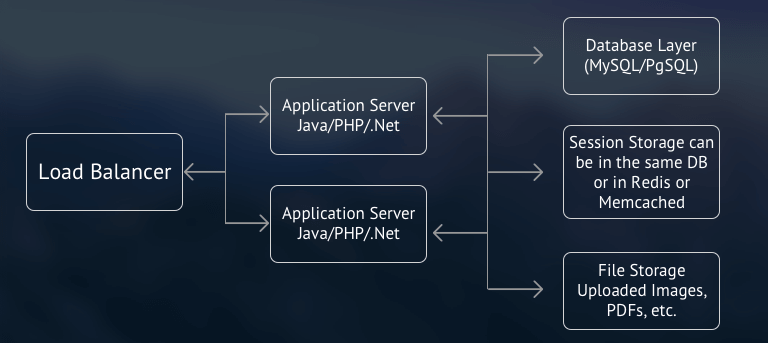 To achieve horizontal scalability in your application, you can follow Shared Nothing architecture at application server level. In short, you move the shared resources to their own servers and make them available to all the application servers over the network. Mainly, you move sessions to a centralized server. This can be stored in the DB for smaller applications. However, since session check happens frequently, this puts unnecessary load on the DB server.
To solve this, you can store sessions in an in-memory cache such as Redis or Memcached. Since data is stored in RAM, it can be accessed quickly. To solve the file storage problem in a traditional data center, you can use NAS (Network Attached Storage) which can be mounted on all application servers. In modern cloud deployments, you have an object store like S3 which provides highly scalable file storage as service. (If you note, S3 itself follows shared nothing architecture which allows it to scale infinitely.) The obvious limitation of this architecture is that its scalability is limited by the scalability of the DB server. However, there are certain things that you can do to scale this architecture further.
Most of the web applications have some sort of search feature. Typically, this search feature requires a lot of expensive queries. You can offload this search load from your DB by using a dedicated search system. For example, Solr or ElasticSearch. Another improvement that can be done is using an in-memory cache in front of your database. For example, if a record hasn't changed since the last fetch, you can simply pull it from the cache, instead of DB. While using such a cache you must make sure that cache is properly invalidated when a DB record is updated. This can be sometimes a bit tricky to get right.
To achieve horizontal scalability in your application, you can follow Shared Nothing architecture at application server level. In short, you move the shared resources to their own servers and make them available to all the application servers over the network. Mainly, you move sessions to a centralized server. This can be stored in the DB for smaller applications. However, since session check happens frequently, this puts unnecessary load on the DB server.
To solve this, you can store sessions in an in-memory cache such as Redis or Memcached. Since data is stored in RAM, it can be accessed quickly. To solve the file storage problem in a traditional data center, you can use NAS (Network Attached Storage) which can be mounted on all application servers. In modern cloud deployments, you have an object store like S3 which provides highly scalable file storage as service. (If you note, S3 itself follows shared nothing architecture which allows it to scale infinitely.) The obvious limitation of this architecture is that its scalability is limited by the scalability of the DB server. However, there are certain things that you can do to scale this architecture further.
Most of the web applications have some sort of search feature. Typically, this search feature requires a lot of expensive queries. You can offload this search load from your DB by using a dedicated search system. For example, Solr or ElasticSearch. Another improvement that can be done is using an in-memory cache in front of your database. For example, if a record hasn't changed since the last fetch, you can simply pull it from the cache, instead of DB. While using such a cache you must make sure that cache is properly invalidated when a DB record is updated. This can be sometimes a bit tricky to get right.
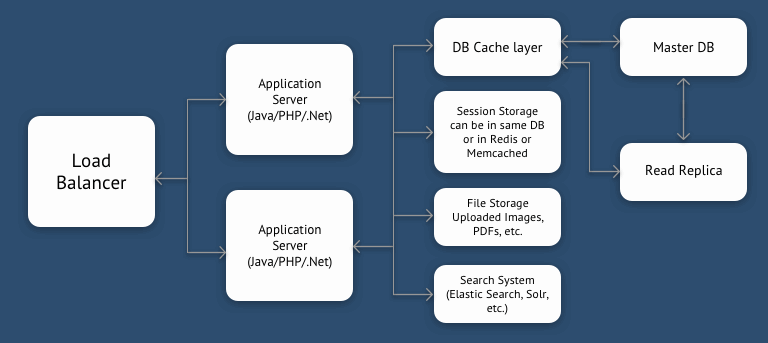
Shared Nothing with Cache and Search System
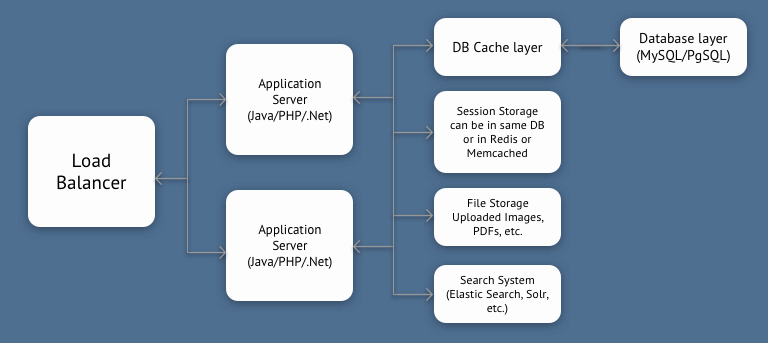 As shown in the figure above, you can reduce the load on DB server by separating the Search System and using a cache layer in front of the database. Though this is still limited by a single DB server capacity, it can take you very far, with a beefy DB server. In fact, this is the architecture Stack Overflow uses. StackOverflow is in Top 100 sites globally.
As shown in the figure above, you can reduce the load on DB server by separating the Search System and using a cache layer in front of the database. Though this is still limited by a single DB server capacity, it can take you very far, with a beefy DB server. In fact, this is the architecture Stack Overflow uses. StackOverflow is in Top 100 sites globally.
Stack Overflow Architecture
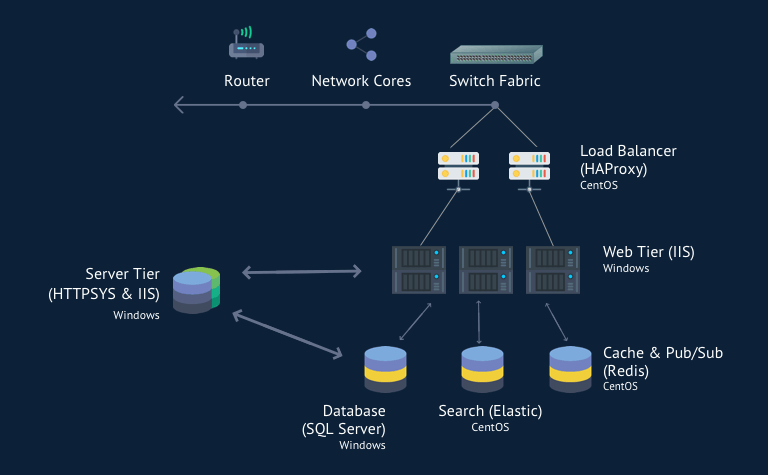
Shared Nothing with Read Replicas for DB
 Most of the web applications are read-heavy. It is said that read-write ratio for most of the Web applications is around 90:10, i.e. for every 8-9 read queries you will have 1-2 write queries. In such case, if one DB is not able to handle the read load then you can create multiple read replicas of your DB. You need to change your application in such a way that write queries go to the master DB and read queries go to read replicas. There are some tools out there which work as a proxy between your application server and your DB cluster. These proxies can automatically route the read-write queries to appropriate servers. This way, you can scale your application even further.
Most of the web applications are read-heavy. It is said that read-write ratio for most of the Web applications is around 90:10, i.e. for every 8-9 read queries you will have 1-2 write queries. In such case, if one DB is not able to handle the read load then you can create multiple read replicas of your DB. You need to change your application in such a way that write queries go to the master DB and read queries go to read replicas. There are some tools out there which work as a proxy between your application server and your DB cluster. These proxies can automatically route the read-write queries to appropriate servers. This way, you can scale your application even further.

 February 7, 2018
February 7, 2018


