With each day passing, we hear news of new technologies all set to revolutionize transportation and logistics industries. Most of these developments involve ground transportation, but there are plenty of technological innovations underway for the ocean freight sector as well. One such technology is ocean freight routing, which in a nutshell, allows you to know the best way to route your shipment. In this article, we will do an in-depth analysis of the ocean freight routing industry and how it has changed the dimensions of the shipping industry.
Ocean Freight Shipping: An Industry Overview
The global logistics market is on the rise and is expected to attain a market size of $12,256 billion by 2022 at a CAGR of 3.48 percent. Although the freight industry is led by the trucking sector, the ocean freight market is also expected to achieve a global market size of 72 million TEUs by 2022.
Ocean freight shipping refers to the transportation of goods that are packed into massive cargo containers and moved by ship. These shipments are typically picked by vessels at ports or airports, and transported through specific shipping lanes.
International shipping is the process of importing and exporting goods from between different countries via ocean, air, or road. It can be a complicated business as it consists of various rules and policies. And, if you are doing it for the first time, it can be a complex arrangement. In general, international shipping consists of the following parts:
- Export Haulage: The freight moves from its origin-destination to the next warehouse from where it will depart to the border.
- Export Customs Clearance: The process of approval once the cargo reaches the border of another country.
- Transportation: It begins once the load has successfully left the origin country.
- Import Customs Clearance: The process of consent once the freight reaches the importing country.
- Import Haulage: The cargo is moved from the border to its final destination.
Types of Ocean Freight Shipping
Ocean freight shipping is primarily divided into two types.
Full Container Load (FCL): In FCL shipping, the shipping costs are calculated by the container, and the shippers are charged one flat rate per full container. In terms of inventory size, you must be able to pay and accommodate the entire container. It gets delivered more quickly because the custom and inspection procedures are more simple and straightforward. Moreover, it works out cheaper per unit. Plus, importing fees are also fixed and do not scale with volume, so the payment is the same irrespective of size. Lastly, the chance of damage is low in FCL as the container just contains goods.
Less Than Container Load (LCL): In LCL, you will be charged by cubic meter if your shipment does not fill the entire container. If not, your shipment will share container space with other shipments. You can make use of LCL consolidation programs to save time and money. Consolidation services are beneficial for businesses that do not have enough cargo for chartering their flight but need to ship smaller quantities of material more often. In head to head with FCL, LCL is more expensive per unit but can turn out to be cheaper overall as the volumes are low. Plus, you can ship smaller amounts, which can be beneficial for cashflow. However, there is a safety risk, as other goods are also supplied with your shipment.
Key Factors Affecting Ocean Freight Rates

Several factors can affect ocean freight rates, such as:
- Destination: Less common destinations have higher costs
- Bunker Fluctuations: Fuel costs impact the overall cost of ocean freight rates
- Seasons: There are two main seasons during the shipping year: mid-August to mid-October and January-February. At this time, the demand for cargo space is high, and supply is low, which leads to a surge in prices. Prices also depend on environmental conditions.
- Service Charges: Terminal fees are charged at the ports of arrival and departure.
- Currency: USD is the standard currency for international transactions, and in a global market, currency exchange fluctuations can influence the ocean freight rates.
- Container Capacity: Ocean shipments are calculated based on weight or measure, whichever is greater. The cost also depends on whether you have opted for FCL or LCL.
Ocean Freight Routing
Ocean route or a sea lane sea road, or shipping lane, is a term used to describe the route for vessels on seas, oceans, or large lakes. The longest known ocean route in the world is from Pakistan to northeastern Russia, measuring a distance of 32,090km. Here are some of the most important ocean freight shipping routes in the world.
- Asia – Australia: Australia to the Asian coast (China, India)
- Asia – South America: Indian and Atlantic oceans
- North America – South America
- Strait of Hormuz: the Middle East and Asia (the Persian Gulf and the Indian Ocean)
- Strait of Malacca: the Pacific Ocean and the Indian Ocean
- South Atlantic Route: West Indies, Brazil, and Argentina to Europe
- Trans-Pacific Route: North America and eastern Asian coast
- Cape Route: Europe, Asia, South America, and Africa
- Panama Canal Route: Atlantic to Pacific Oceans
- Suez Canal Route: Europe to Asia (Mediterranean Europe with the Indian Ocean)
- North Atlantic Route: European and North American ports
Ocean freight routing is defined as a system of ocean freight shipping by fixed container shipping routes from one or several railroad stations to a destination. Ocean freight forwarding is a subset of the broader concept: freight routing. The purpose of routing is to help carry forward a quick inbound receipt that reduces time, cost, and confusion when a shipment is delivered to the shipper's inbound shipping dock.
Ocean freight routing is further divided into:
Ship Routing: It is used to improve the safety of navigation in areas of high traffic or where the freedom of movement of shipping is restricted.
Container Routing: It determines how containers should be transported from their origins to the destination.
Weather Routing: It consists of using actual weather and forecast weather to develop the best route. It makes use of weather forecasts, ship characteristics, special cargo requirements, and ocean currents.

Trends and Possibilities in the Ocean Freight Shipping Sector
Lots of innovations are currently being tested and implemented in the ocean freight transportation sector. Companies like IBM and Maersk are partnering to offer an exhaustive exchange of shipping information built upon blockchain. Reports of adoption of operating platforms like N4 and XVELA are also underway, which enable ships to exchange information in a shared cloud application.
Soon, we can also witness fully-autonomous cargo ships that use a combination of radar, cameras, sensors, and GPS. Also, much of the future technology in ocean freight shipping will aim to reduce its environmental impact. Ocean freight shipping is a significant contributor to pollution, and tech may be the best solution to assist the pollution problem.
Ocean Freight Route Planner
An ocean freight route planner enables you to facilitate ocean freight routing, vessel routing, weather routing, and passage planning, thereby helping you calculate the fastest route you can take from point A to point B. It takes into account the current weather forecast, oceanic currents, vessel performance, and comfort criteria to suggest the best possible route. One such tech-friendly solution is the ocean freight route planner.
How It Works?
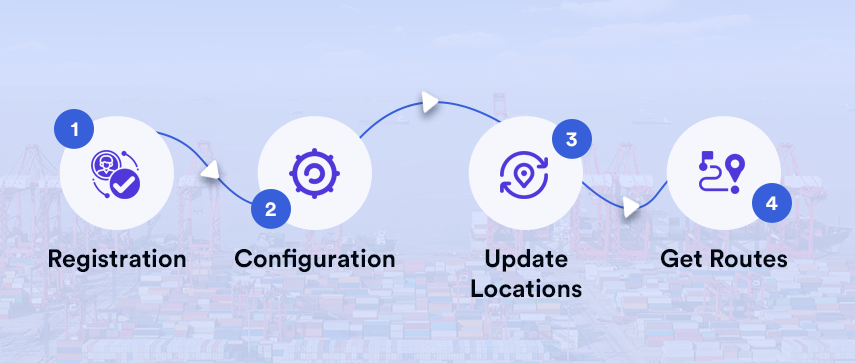
Here is a quick guide to how an ocean freight route planner works.
- Registration: First and foremost, you will need to sign up and log in to your account, which allows the system to store your polar and comfort criteria.
- Configuration: After logging in, you will need to update the performance characteristics of your vessel. Several factors are taken into consideration to determine the overall performance of your vessel.
- Update Locations: Now, set your origin and destination. You can either manually enter the places or mark them on the map.
- Get Routes: Now, you can let the system calculate the best route for you. After calculation, your route will be displayed on the map. You can get further insights by specifying factors like your comfort criteria, maximum wind speed, reaching, and maximum gust conditions.
Key Features
Features of an ocean route planning software can vary, but here are a bunch of key features to look for.
i Powerful Route Optimization Engines
The system should be able to consider the parameters that drive your business. Planning tools have a robust optimization engine, which seamlessly handles several business parameters and produces feasible results.
ii Ergonomic User Interface
A planning tool consists of an ergonomic and intuitive user interface. Thus, even if you do not have any knowledge of information technologies, you will be able to quickly adapt to the system and produce results easily and quickly.
iii Intelligent, High-resolution Maps
High-resolution maps are one of the critical features every routing software offers. These maps include up-to-date information regarding multiple data layers, such as congestion, traffic, weather, and so on. It helps you get in-depth information on your shipping route, making it easy for you to plan further.
iv Dispatch Management and GPS Tracking
Ocean freight solutions offer effective fleet operations by providing flexibility to adjust and respond to daily realities once a ship embarks from the port. The system continuously measures Plan vs. Route Performance to meet customer expectations and achieve maximum productivity.
v Open, Robust Architecture
An ocean planning system integrates with your existing IT setup, along with interoperating with all of your Transport Management, Enterprise Resource Planning, Sea Freight Tracking, and Warehouse Management systems.
Why Choose an Ocean Freight Route Planner?
An ocean freight route planner can add significant value to fleet managers and the entire organization. Here are a few reasons why you should choose an ocean freight route planner.
1 Reduced Monetary Investment
Routing software uses advanced algorithms to determine the best, cost-effective routes. They create routes based on schedule constraints and fleet availability. These tools intelligently assign resources to reduce the overall fleet time in the ocean. It, in turn, leads to:
- Reduced fuel costs
- Reduced vehicle maintenance costs
- The reduced total cost of ownership
- Lowered accidents, violations, and associated costs
- Increased responsiveness to last-minute schedule changes
When an order is urgent, or jobs take longer than expected, the route assignment is required. Ocean freight shipping services can integrate with dispatching and scheduling software to help you proactively plan new routes without any hassle. Thus, it helps you make quicker decisions, which leads to enhanced consumer experience.
2 Increased Completed Jobs
The Logistics industry is a numbers game; the more tasks you complete, the more revenue you will generate, and the more profits you will earn. However, an increased number of jobs can exhaust your staff, and can also result in reduced efficiency. A routing planner helps you overcome this hurdle by ensuring that a fleet's route is efficient in terms of time to delivery and route optimization. Thus, the service time is reduced, and companies can increase the number of jobs they perform in an effective, sustainable manner.
3 Quicker Route Planning
Route planning solutions can reduce the amount of time fleet managers spend on trip planning. Planning ocean routes is becoming more complex, with traffic flow rapidly increasing; thus, it is crucial to have a system that helps you determine the best routes for each destination.
4 Reduced Transportation Delays
Traffic bottlenecks can be a significant problem for ships too, and it seems to increase over time. Recent reports suggest that traffic congestion costs thousands of dollars per shipment per year to fleet operational costs. A route planning system helps you to reduce these costs by improving your plan, less busy routes, and shortening transport time. It also enables fleet managers to assist their drivers concerning day-to-day logistic problems.
Conclusion
With the costs and congestion of air and road transport increasing, ocean freight transportation is one of the most feasible and cost-effective ways to ship items and packages across borders. However, when the number of shipments surges, there rises a need for a system that guarantees efficiency and productivity, which you can achieve with an ocean route planning solution. So, if you are a fleet manager or the owner of an ocean freight company and struggling with the reducing efficiency and increasing workload, try bringing an ocean route planning system to your deck.





 March 26, 2020
March 26, 2020


