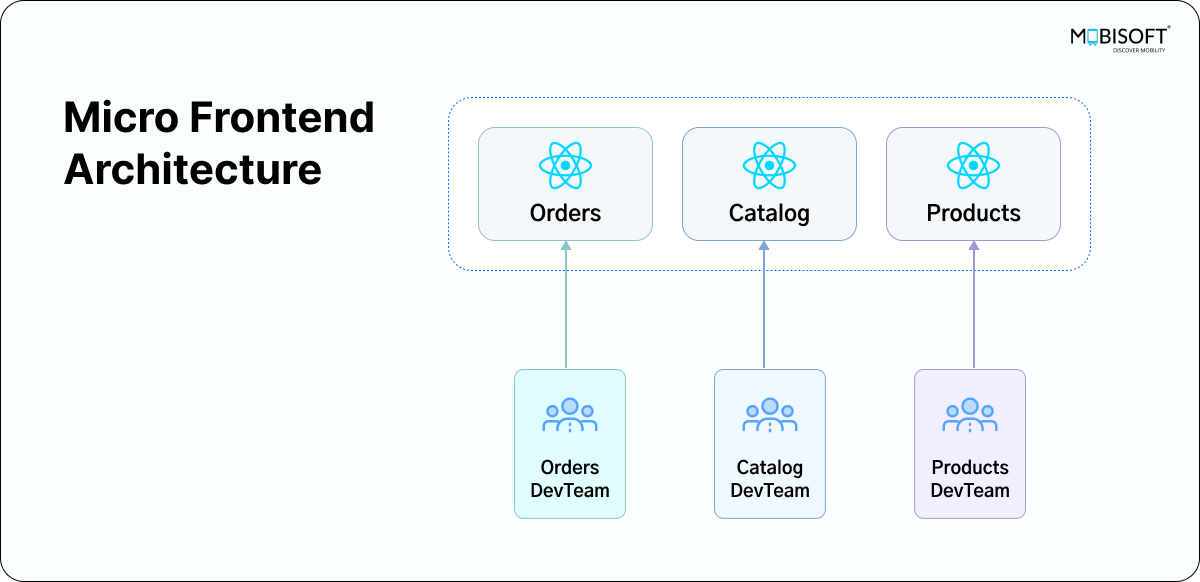
Why Micro-Frontends?
Micro frontend architecture is becoming increasingly popular due to its performance benefits and the ability to reduce developer dependencies. By breaking down a monolithic frontend into smaller, independent micro-applications, teams can work on different parts of a project simultaneously, improving scalability and maintainability.
What You Will Learn in This Tutorial
In this guide, we will walk through the process of setting up a micro-frontend architecture using React and Vite. You will learn:
- How to configure Module Federation with Vite.
- How to create a remote micro-frontend that exposes components.
- How to dynamically reuse a remote component in a host application.
Project Use Case: E-Commerce Application
For this tutorial, we will use an e-commerce application as an example. The host application (home app) will consume and display a Featured Products List from the Products Micro-Frontend. This approach showcases how a fully functional component can be shared across multiple applications without duplicating code.
By the end of this tutorial, you will have a clear understanding of how to structure a micro-frontend application with React and Vite, making your micro frontend architecture more flexible and scalable.
Setting Up the Microfrontend Project
Create the Main Directory
mkdir micro-frontend-project
cd micro-frontend-project
Create two separate Vite projects:
- Products (Remote App) → Micro-frontend exposing a component.
- Host (Main App) → Application consuming the remote component.
Setting Up the Remote Products Feature
Step 1: Create the Products Project
npm create vite@latest
- Enter project name:
products - Select
React - Select
TypeScript

Step 2: Install Module Federation Plugin
cd productsnpm install @module-federation/vite
Step 3: Implement Product List Feature
1. Create Product List Page:
Create src/pages/ProductsList/ProductsList.tsx to display featured and all products.
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import { ProductListItem } from "../../components/ProductListItem/ProductListItem";
import { IProduct } from "../../interfaces/IProduct";
import "./ProductsList.css";
import FeaturedProductsList from "../../components/FeaturedProductsList/FeaturedProductsList";
export const ProductList = () => {
const [products, setProducts] = useState<IProduct[]>([]);
useEffect(() => {
fetchProducts();
}, []);
const fetchProducts = async () => {
try {
const productsResponse = await fetch("https://dummyjson.com/products");
const productsResponseJson = await productsResponse.json();
setProducts(productsResponseJson.products);
} catch (error) {
console.log("error", error);
}
};
return (
<div className="product-list-container">
<h2>Products</h2>
<FeaturedProductsList></FeaturedProductsList>
<h2 className="heading">All Products</h2>
<div className="products-list">
{products.map((item) => (
<ProductListItem product={item}></ProductListItem>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
};
Here, we are using a dummy API for the product list.
2. Create Product List CSS:
Create src/pages/ProductsList/ProductsList.css
.products-list {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: repeat(auto-fit, minmax(300px, 1fr));
grid-auto-rows: minmax(250px, auto);
}
.product-list-container {
height: 100vh;
width: 100%;
text-align: flex-start;
}3. Create Product Interface:
Create src/interfaces/IProduct.ts
export interface IProduct {
title: string;
description: string;
price: string;
images: string[];
}4. Create Product Card Component:
Create src/components/ProductListItem/ProductListItem.tsx
import { IProduct } from "../../interfaces/IProduct";
import "./ProductListItem.css";
interface ProductListItemProps {
product: IProduct;
}
export const ProductListItem = (props: ProductListItemProps) => {
const { product } = props;
return (
<div className="product-card">
<div className="product-image-container">
<img src={product.images[0]} className="product-image"></img>
</div>
<h3>{product.title}</h3>
<h2>{`$ ${product.price}`}</h2>
<h6>{product.description}</h6>
</div>
);
};5. Create Product Card CSS file:
Create src/components/ProductListItem/ProductListItem.css
.product-image {
width: 120px;
height: 120px;
}
.product-card {
background-color: white;
border-radius: 4px;
box-shadow: rgba(100, 100, 111, 0.2) 0px 7px 29px 0px;
padding: 8px;
margin: 8px;
min-width: 285px;
}
.product-image-container {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}6. Create Featured Product List Component:
Create src/components/FeaturedProductsList/FeaturedProductsList.tsx
import { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import { IProduct } from "../../interfaces/IProduct";
import { ProductListItem } from "../ProductListItem/ProductListItem";
import "./FeaturedProductsList.css";
const FeaturedProductsList = () => {
const [featuredProducts, setFeaturedProducts] = useState<IProduct[]>([]);
useEffect(() => {
fetchProducts();
}, []);
const fetchProducts = async () => {
try {
const productsResponse = await fetch('https://dummyjson.com/products?limit=10&skip=10&select=title,price,images,description');
const productsResponseJson = await productsResponse.json();
setFeaturedProducts(productsResponseJson.products);
} catch (error) {
console.log("error", error);
}
};
return (
<div>
<h2 className="heading">Featured Products</h2>
<div className="featured-product-list">
{featuredProducts.map((item) => (
<ProductListItem product={item}></ProductListItem>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default FeaturedProductsList;7. Create Featured Product List CSS file:
Create src/components/FeaturedProductsList/FeaturedProductsList.css
.featured-product-list {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
overflow-x: scroll;
}8. Use the Products page in the App file:
import './App.css'
import { ProductList } from './pages/ProductsList/ProductsList'
function App() {
return (
<>
<ProductList></ProductList>
</>
)
}
export default App9. Update App.css default CSS:
Update only root css
#root {
max-width: 1280px;
padding: 2rem;
height: 100vh;
}10. Update port in the package.json:
...
"scripts": {
"dev": "vite --port 3000",
"build": "tsc -b && vite build",
"lint": "eslint .",
"preview": "vite preview --port 3000"
},
...Step 4: Configure Module Federation
Update vite.config.ts
import { federation } from "@module-federation/vite";
import react from "@vitejs/plugin-react";
import { defineConfig } from "vite";
import { dependencies } from "./package.json";
export default defineConfig(() => {
return {
build: {
target: "chrome89",
},
plugins: [
federation({
filename: "remoteEntry.js",
name: "products",
exposes: {
"./featured-products":
"./src/components/FeaturedProductsList/FeaturedProductsList.tsx",
},
remotes: {},
shared: {
react: {
requiredVersion: dependencies.react,
singleton: true,
},
},
}),
react(),
],
};
});filename:"remoteEntry.js": Specifies the entry file for the microfrontend, which other applications can access.name: "products": Defines the unique identifier for this microfrontend.- This allows other microfrontends (hosts) to import the FeaturedProductsList component.
"./featured-products": This is how the module will be imported remotely."./src/components/FeaturedProductsList/FeaturedProductsList.tsx": The actual file that gets exposed.
Setting Up the Host Application
Step 1: Create the Host Project
npm create vite@latest
- Enter project name:
host - Select
React - Select
TypeScript
Step 2: Install Module Federation Plugin
cd hostnpm install @module-federation/vite
Step 3: Implement Home Page
1. Create Home Page:
Create pages/home/Home.tsx
import React, { Suspense } from "react";
const FeaturedProducts = React.lazy(
// @ts-ignore
async () => import('products/featured-products'),
);
const Home = () => {
return (
<div>
<h2>Home</h2>
<Suspense fallback="loading...">
<FeaturedProducts />
</Suspense>
</div>
);
};
export default Home;Imported Featured Products from Products (Remote app)
2. Update App.tsx
import "./App.css";
import Home from "./pages/home/Home";
function App() {
return <Home></Home>;
}
export default App;3. Update App.css default CSS:
Update only root css
#root {
max-width: 1280px;
padding: 2rem;
height: 100vh;
}Step 4: Configure Module Federation
Update vite.config.ts
import { defineConfig } from "vite";
import react from "@vitejs/plugin-react";
import {federation} from "@module-federation/vite";
import { dependencies } from './package.json';
// https://vite.dev/config/
export default defineConfig({
build: {
target: 'esnext',
minify: false
},
plugins: [
federation({
name: "app",
remotes: {
products: {
type: 'module',
name: 'products',
entry: 'http://localhost:3000/remoteEntry.js',
entryGlobalName: 'remote',
shareScope: 'default',
},
},
filename: "remoteEntry.js",
shared: {
react: {
requiredVersion: dependencies.react,
singleton: true,
},
},
}),
react(),
],
});remotes: Specifies the remote applications (microfrontends) that will be loaded dynamically.products: The key that identifies the remote application.type: 'module': Indicates that the remote entry is an ES module.name: 'products': The unique name of the remote application.entry: 'http://localhost:3000/remoteEntry.js': The remote entry file URL where the microfrontend is hosted.entryGlobalName: 'remote': Specifies a global namespace for the remote module.shareScope: 'default': Ensures dependency sharing across microfrontends.
shared: Specifies shared dependencies across microfrontends to avoid duplicate React versions.
Final Steps: Run Both Applications
Run the Remote App (Products)
cd productsnpm run dev
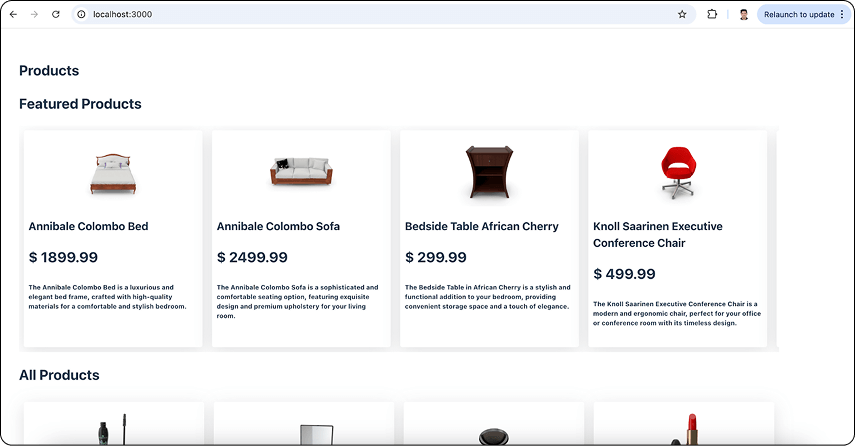
On http://localhost:3000/, you can see the featured products and a list of all products.
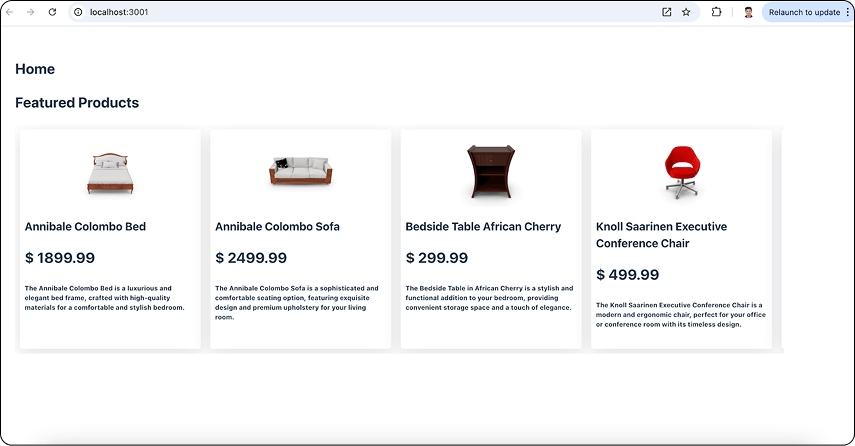
Run the Host App
cd host npm run dev
Now, the Host Application dynamically loads the Featured Products Component from the Products Micro-Frontend using vite module federation
This repository contains the code for the tutorial: “React Micro Frontend Architecture – An in Depth Tutorial With Example“, published by Mobisoft - Web Application Development Company, Houston.
Feel free to download a sample example I’ve created from GitHub to get started.
Conclusion
Micro-frontend architecture is revolutionizing front-end development by enabling teams to work independently on different parts of an application while ensuring seamless integration. In this tutorial, we explored how to set up a micro-frontend architecture using React, Vite, and Module Federation, allowing components to be dynamically shared across multiple applications.
By implementing a Products Micro-Frontend and a Host Application, we demonstrated how to reuse a fully functional component (Featured Products List) without duplicating code.
This approach makes frontend development scalable, modular, and efficient, reducing dependencies between teams and improving performance. With micro-frontends, applications can be developed and deployed independently, making them easier to maintain and extend over time.




 February 25, 2025
February 25, 2025


