The ability to communicate and adequately share patient information through different IT channels has gained undeniable importance in the current medical industry. Providing support in breaking organizational barriers, interoperability can help in adding value to healthcare. It can provide better outcomes for patients along with a host of other benefits for healthcare providers.
With serious untapped potential, interoperability is one of the most underutilized concepts in the healthcare structure of the world. Eliminating room for error and making healthcare dynamics more dependable is what needs to be stressed on. With the healthcare industry becoming more complex and diverse each day, there is a need for an appropriate management system to simplify things for the people involved. This includes everyone, right from the lesser-educated patient who may be unfamiliar with medical terminology to the doctor who struggles to find the time to look for a patient’s previous records.
What Is Interoperability in Healthcare? The Relationship between Health Data and Health IT Interoperability
Interoperability in healthcare is what a summary of a book is for a reader. It compiles the entire information and presents it in a crisp, simplified, and understandable way. Similarly, interoperability is the process of gathering patient information from multiple databases and presenting it to the healthcare provider. This makes it easier for them to access the patient’s medical history and condition.
Adequate Health Information Exchange

Health information exchange needs to be seamless; it is divided into several crucial steps like procuring, sending, receiving, and assimilating. If any of these steps is not considered adequately or missed, the healthcare provided to the patient, and the productivity of the healthcare providers may get affected.
Surveys reveal that transfer of information is more manageable than receiving and integrating it. The sizes of healthcare-providing organizations differ and so do their channels of data-based information. It means that while information may be available on cloud storage, it may be of little or no use to a rural healthcare provider because they won’t be able to retrieve it promptly. This raises the need for uniformity across all channels of healthcare database management through different organizational sizes and types. Streamlining it might enable a similar standard of healthcare in a rural clinic as a cosmopolitan hospital.
Accuracy and Reliability
There were times when word of mouth or handwritten notes on a patient’s condition were used to fill out forms and to plan the course of action for treatment. With the introduction of direct electronic means of data-keeping, things have been steadily becoming more dependable. When you visit a doctor now, you may be asked to fill out forms on a tablet. This only suggests that there is direct electronic storage of our data, making it easily retrievable, transferable, and smoother to use for the doctors as well as patients.
Today, there are databases that doctors can log on to and access the case history of a patient. The accuracy of this type of data-keeping is what has made interoperability such a widely accepted phenomenon. The health information exchange is a broad spectrum of data that needs to be kept and studied by the healthcare provider from time to time during the course of the treatment. This includes a clinical summary, list of medications, lab test results, and so on.
Better Scenario in Hospitals than Private Practices
The size of the data to be managed and retrieved daily in hospitals is in abundance, which makes the need for proper electronic record-keeping a necessity. However, when it comes to office-based physicians or individual practitioners, there is a lack of proper record-keeping. The information is not adequately shared with users outside of their organization and this makes it difficult for the best healthcare to reach the patient in times of need.
Let’s assume that you happen to change doctors at any point in your treatment. Now, the new doctor will have to run the same number of extensive tests to determine your current condition to treat you accurately. This only indicates wastage of time, effort, and money—time being of crucial importance when it comes to healthcare.
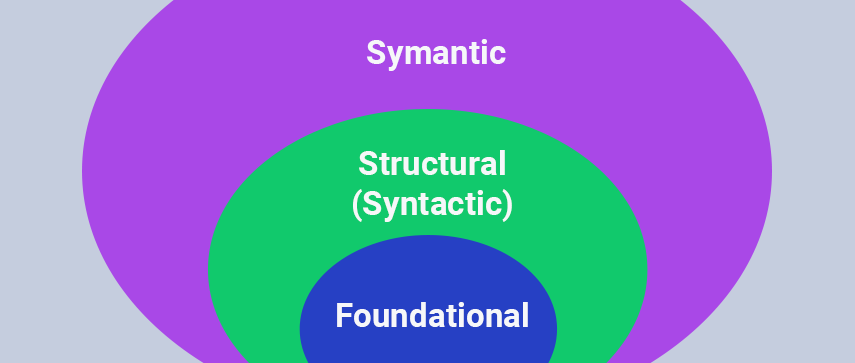
There Are Different Levels of Interoperability—Each of Critical Importance. Let’s Have a Look:
1 Foundational Interoperability
This offers the most basic level of exchange of information through different channels. This level enables the HIT information transition from one channel to another. It, however, doesn’t require the receiving end of the information to interpret it immediately. This could be thought of as the base of the interoperability pyramid. Proper record-keeping of each patient will help in a better study of their medical history when required; the first level of interoperability constitutes just that.
2 Structural interoperability
The format of the exchange of data is to be determined at this level. The structure of the message needs to be such that the receiver can interpret it with ease and use it to provide the best healthcare to the patient. This allows a smooth and uniform movement of health data from one end to another. However, health data cannot be standardized, which is what makes further analysis essential.
3 Semantic Interoperability
The highest element of the interoperability chain contains coded streamlined data. This, in turn, allows an improvement in the interpretation of HIT data. The purpose of this step is to create a perfect machine-to-machine data transfer channel that is reliable and accurate. The most important part of this is data normalization. This standardization of the various terms, phrases, and types of data stored facilitate communication in the best possible way. The data has to go through different format changes or terminology changes to be saved and transmitted in a uniform pattern so that it is retrievable by the other party. It changes local content into standard terminologies and enables the semantic translation of data to eliminate any relative ambiguity.
Why Is Interoperability Important? What Are the Benefits of Healthcare Interoperability?
With the changing times, the need for being connected uninterruptedly has grown in all fields—healthcare being one of them.
“Interoperability describes the extent to which systems and devices can exchange data, and interpret that shared data. For two systems to be interoperable, they must be able to exchange data and subsequently present that data such that it can be understood by a user,” as explained by the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society.
The capacity of utilizing software and computers to share as well as exchange data from vital sources such as hospitals, pharmacies, laboratories, medical practices, and so on is of primary importance in healthcare interoperability.
1 Improving Patient Experience

If your physician were to send you for an MRI scan, the radiographers or radiologists would be able to share your reports almost immediately even if they don’t use the same software internally. This sort of uniformity in transmission and reception of information can be of vital importance in the course of healthcare provided to a patient.
2 Saves Time
The time taken in the useful transfer of information between two healthcare professionals or a healthcare professional and a patient can be reduced manifold with adequate interoperability.
3 Simplifying Health Records
When a healthcare provider treats a patient well, they will recommend them to others, and client testimonials are of great importance in healthcare. When there is better patient engagement, more time can be given to the actual process of planning a course of action for their health instead of repeatedly running the same tests and waiting for the patients to find their previous prescriptions.
4 Lowering Costs
When interoperability enables the transfer of accurate information from one channel to another, the cost incurred in medical treatments becomes relatively lower.
5 Helpful in Dynamic Situations
This is very helpful in cases where a person is traveling out of town and needs a doctor’s consultation or when a person needs to change the doctor during their treatment of a chronic illness. Considering how costly and time-consuming scans and tests may be, interoperability is a brilliant step to save energy and money.
6 Better Healthcare Transition
When you move to a different location or need to change your healthcare providers for any reason, interoperability could be of great help. You may forget the details of the line of treatment given to you over the time, the name of the medicines, the kind of changes it brought about in your condition, and your respective relevant blood report. However, if there is a proper electronic database, the new doctor will be able to pick up right where the previous doctor left.
7 Maintains Patient Privacy
An essential aspect of healthcare—the right to doctor-patient privacy—can benefit tremendously by the use of interoperability. Cutting the need for clinical staff and manually updating patient records from untidily scribbled prescriptions, patient privacy can be maintained well if there is accurate electronic data management initially performed.
8 Reduction in Errors
Needless to say, there is a need for accuracy in the healthcare setup. Data-entry can be unintentionally distorted when performed manually. Small and slight errors can occasionally pose serious health threats. A person may enter the wrong blood group or incorrectly mark a report as negative and vice-versa. These errors may seem small but they could make a life-altering difference. These risks can be avoided with reliable interoperability.
9 Better Record-Keeping of Healthcare Data (Public)
Important while studying tendencies of ailments and the effect a particular medicine on a set of patients, interoperability provides an adequate database to aid studies and development of new healthcare trends. It contributes to the bigger picture while also helping patients on a day-to-day basis.
Interoperability – A Game Changer for the Future of Healthcare

The current transitional changes in the healthcare industry indicate an urgent need for appropriate interoperability. According to the 21st century Cures Act, [5] rules proposed by the ONC as well as the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resource data standard, there are some stringent measures to be taken to conquer the lack of proper electronic data management in the near future.
According to HL7; a company providing guidelines and standards on interoperability, the HL7V3 standard was released in 2005 works in accordance with the XML syntax. This standard is used by many countries at the national level. DICOM and HL7 work hand in hand for the coexistence of these two standards to benefit interoperability in the long run.
With local and regional healthcare institutes building the cornerstone for an interoperability-driven future, it seems things are going to look better in the time to come. With the hope of streamlined, better-managed healthcare industry, each organization or individual practitioner needs to take the first step toward creating an interoperable coexistence.
It is time all small and large healthcare entities take it upon their shoulders to create a tomorrow that is close-knit and interoperability of high importance in order to provide the best care and attention to the patients in times of need.





 May 27, 2019
May 27, 2019


