Introduction
What if your iOS app could write stories, summarize long documents, pull out key details, or even translate languages without ever touching the cloud? With iOS 26 and Apple’s new Foundation Models, that’s no longer science fiction. In this guide, I’ll show you how to tap into Apple Intelligence to build smarter, privacy-first apps that run entirely with on-device AI. Along the way, we’ll put together a demo app that highlights multiple Apple AI features, from text generation to content classification, so you can see exactly how these capabilities come to life on iOS.
To build future-ready and intelligent Apple-based applications, explore our iOS app development services designed for performance, scalability, and innovation.
Why On-Device AI Matters?
For years, mobile apps have leaned on cloud-based AI. It is powerful, but it also comes with tradeoffs. Every time data leaves a device, users relinquish a portion of their privacy. Apps break down when the network is weak. Responses feel slower because they are waiting for a round-trip to a server. And for developers, those API calls can quickly add up in cost.
With iOS 26, Apple is flipping that model on its head. Thanks to the Foundation Models framework, advanced Apple artificial intelligence now runs entirely on the device. That means faster responses, apps that work offline, and most importantly, AI experiences that respect user privacy and put control back in their hands.
The combination of Apple machine learning and on-device AI creates a foundation for smarter and more secure mobile experiences. Developers can now harness foundation models AI to deliver intelligent, real-time results without relying on cloud infrastructure.
Want to accelerate your next Apple Intelligence project? You can hire expert iOS app developers who specialize in building AI-driven apps optimized for iOS 26.
What We'll Build
Throughout this guide, we'll create a comprehensive Apple Intelligence app that demonstrates:
- Text Generation: Creative writing and content creation
- Summarization: Condensing long texts into concise summaries
- Task Suggestions: AI-powered productivity recommendations
- Entity Extraction: Identifying people, places, organizations, and events
- Content Classification: Analyzing sentiment, topics, and categories
- Creative Content: Stories, poems, and dialogues
- Translation: Multi-language text conversion
Looking to bring similar intelligent capabilities to your own app? Discover how our mobile app development services can help you design AI-powered experiences tailored to your business goals.

The Technical Foundation
Our app leverages several key iOS 26 technologies:
- Foundation Models Framework: Apple’s on-device AI engine
- @Generable Protocol: Structured output generation for reliable AI responses
- SwiftUI: Modern, declarative UI framework
- LanguageModelSession: Real-time AI interaction management
Apple's AI framework and Apple Intelligence tools provide a powerful foundation for developing intelligent, machine-learning-driven apps on iOS 26. Explore more about Apple Intelligence and its capabilities.
Prerequisites
To follow along with this guide, you'll need:
- Xcode 26 with iOS 26 SDK
- iOS 26.0+ device or simulator
- Basic Swift/SwiftUI knowledge
Let’s Dive In..
Building the AI Manager: The Heart of On-Device Intelligence
Introduction to LocalAIManager
The LocalAIManager is the cornerstone of our Apple Intelligence app. It's responsible for interfacing with Apple's Foundation Models framework and providing a clean, SwiftUI-friendly API for all AI operations powered by on-device machine learning.
1. Core Architecture and Setup
@available(iOS 26.0, *)
class LocalAIManager: ObservableObject {
@Published var isProcessing = false
@Published var lastError: String?
private var session = LanguageModelSession()
private let model = SystemLanguageModel.default
init() {
setupModel()
}
}Key Components:
- ObservableObject: Enables SwiftUI reactive updates
- LanguageModelSession: Manages AI model interactions
- SystemLanguageModel.default: Apple's on-device AI model
- State Management: Tracks processing status and errors
Want professional assistance? Hire mobile app developers experienced in building and deploying AI-driven iOS solutions for diverse business needs.
2. Model Availability and Initialization
private func setupModel() {
// Check model availability
switch model.availability {
case .available:
print("Foundation Model is available")
case .unavailable(let reason):
lastError = "Foundation Model unavailable: \(reason)"
print("Foundation Model unavailable: \(reason)")
}
}
var isFoundationModelAvailable: Bool {
return model.availability == .available
}Purpose:
- Availability Check: Verify if the AI model is available on the device
- Error Handling: Set appropriate error messages when unavailable
- Graceful Degradation: Handle cases where AI features aren't supported
3. Text Generation
func generateText(prompt: String, completion: @escaping (String) -> Void) {
guard case .available = model.availability else {
completion("Foundation Model not available")
return
}
// Sanitize input to prevent safety guardrails
let sanitizedPrompt = sanitizeInput(prompt)
isProcessing = true
lastError = nil
Task {
do {
let response = try await session.respond(to: Prompt(sanitizedPrompt))
let content = response.content
await MainActor.run {
self.isProcessing = false
completion(content)
}
} catch {
await MainActor.run {
self.isProcessing = false
let errorMessage = handleSafetyGuardrailsError(error)
self.lastError = errorMessage
completion("Error generating text: \(errorMessage)")
}
}
}
}Implementation Details:
- Availability Check: Verify the model is available before processing
- Input Sanitization: Clean user input to prevent safety issues
- Async Processing: Use modern Swift concurrency
- Error Handling: Provide user-friendly error messages
Integrating AI into apps requires a balance between robust functionality and seamless user experience. This shift towards experience-led app development is key to creating intuitive and impactful AI-powered apps.
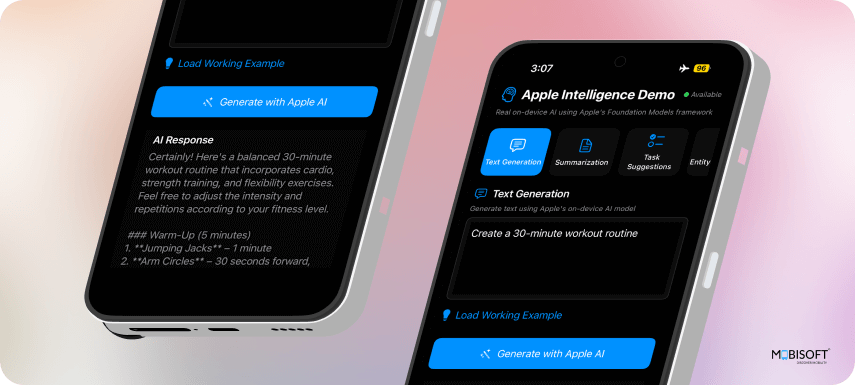
4. Summarization
func summarizeText(_ text: String, completion: @escaping (String) -> Void) {
guard case .available = model.availability else {
completion("Foundation Model not available")
return
}
// Sanitize input to prevent safety guardrails
let sanitizedText = sanitizeInput(text)
isProcessing = true
lastError = nil
Task {
do {
let prompt = "Summarize the following text concisely:\n\n\(sanitizedText)"
let response = try await session.respond(to: Prompt(prompt))
let content = response.content
await MainActor.run {
self.isProcessing = false
completion(content)
}
} catch {
await MainActor.run {
self.isProcessing = false
let errorMessage = handleSafetyGuardrailsError(error)
self.lastError = errorMessage
completion("Error summarizing text: \(errorMessage)")
}
}
}
}Features:
- Content Compression: Reduces text length while maintaining key information
- Context Preservation: Keeps important details in the summary
- Consistent Prompting: Uses clear instructions for reliable results
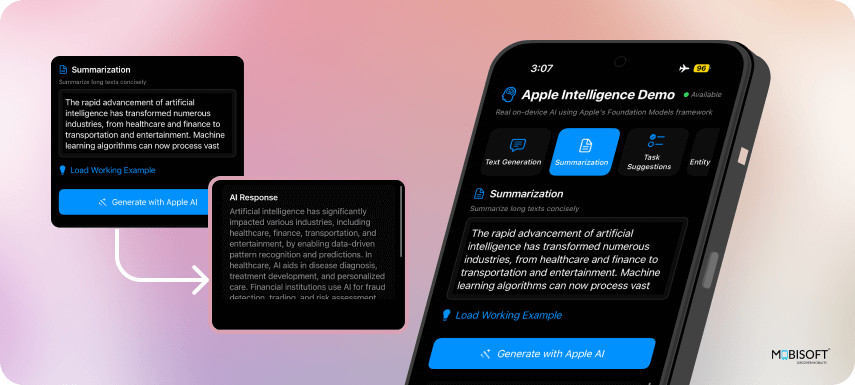
5. Structured Generation with @Generable
@Generable is a Swift macro that tells Apple’s Foundation Models framework to generate structured data matching your Swift struct. Instead of getting raw text from the AI, you get back properly typed objects, a significant advantage when working with machine learning on iOS.
TaskSuggestion Struct
@Generable
struct TaskSuggestion {
let title: String
let description: String
let category: String
let priority: String
}What it does:
- Defines Structure: Tells the AI exactly what fields to include
- Type Safety: Ensures the AI response matches this exact format
- Automatic Parsing: Foundation Models converts AI responses into this struct automatically
Task Suggestions
func generateTaskSuggestions(from text: String, completion: @escaping ([TaskSuggestion]) -> Void) {
guard case .available = model.availability else {
completion([])
return
}
// Sanitize input to prevent safety guardrails
let sanitizedText = sanitizeInput(text)
isProcessing = true
lastError = nil
Task {
do {
let prompt = "Based on the following text, suggest 3 actionable tasks:\n\n\(sanitizedText)"
// Use guided generation for structured output
let response = try await session.respond(
to: Prompt(prompt),
generating: [TaskSuggestion].self
)
let content = response.content
await MainActor.run {
self.isProcessing = false
completion(content)
}
} catch {
await MainActor.run {
self.isProcessing = false
let errorMessage = handleSafetyGuardrailsError(error)
self.lastError = errorMessage
completion([])
}
}
}
}Benefits:
- Type Safety: Compile-time validation of AI responses
- Structured Output: Consistent data format for UI consumption
- Automatic Parsing: Foundation Models handles JSON conversion
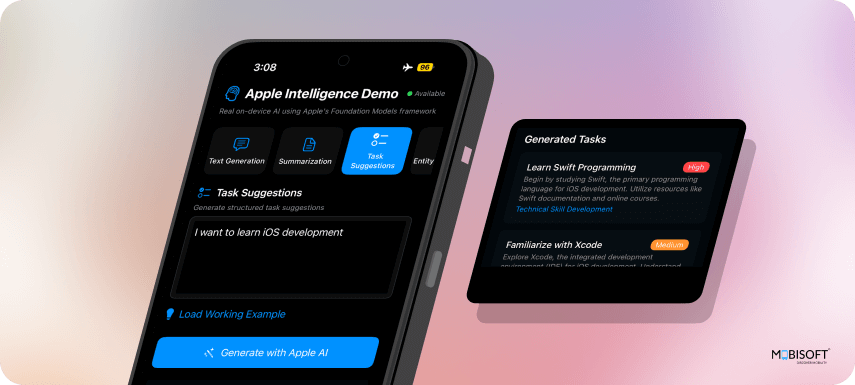
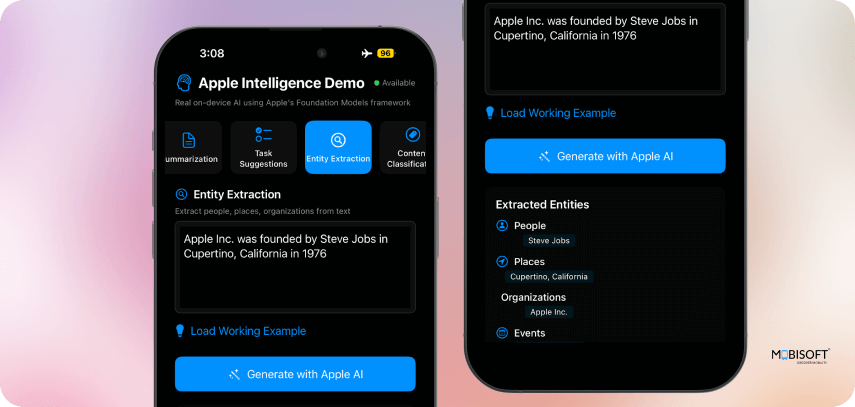
6. Entity Extraction
ExtractedEntities Struct
@Generable
struct ExtractedEntities {
let people: [String]
let places: [String]
let organizations: [String]
let events: [String]
}What it does:
- Entity Categorization: Organizes extracted information into specific categories
- Array-based Fields: Each field contains a list of related entities
- Structured Output: AI response is automatically parsed into categorized arrays
func extractEntities(from text: String, completion: @escaping (ExtractedEntities?) -> Void) {
guard case .available = model.availability else {
completion(nil)
return
}
isProcessing = true
lastError = nil
Task {
do {
let prompt = "Extract entities from the following text and categorize them:\n\n\(text)"
let response = try await session.respond(
to: Prompt(prompt),
generating: ExtractedEntities.self
)
let content = response.content
await MainActor.run {
self.isProcessing = false
completion(content)
}
} catch {
await MainActor.run {
self.isProcessing = false
self.lastError = error.localizedDescription
completion(nil)
}
}
}
}Capabilities:
- Multi-category Extraction: Identifies people, places, organizations, events
- Context Awareness: Understands entity relationships
- Structured Output: Returns categorized entity data
7. Content Classification
ContentClassification Struct
@Generable
struct ContentClassification {
let category: String
let sentiment: String
let topics: [String]
let confidence: Double
}What it does:
- Multi-dimensional Analysis: Captures category, sentiment, topics, and confidence in one structure
- Mixed Data Types: Combines strings, arrays, and numeric values
- Confidence Scoring: Includes a numerical reliability assessment
func classifyContent(_ text: String, completion: @escaping (ContentClassification?) -> Void) {
guard case .available = model.availability else {
completion(nil)
return
}
// Sanitize input to prevent safety guardrails
let sanitizedText = sanitizeInput(text)
isProcessing = true
lastError = nil
Task {
do {
let prompt = """
Analyze the following text and provide:
1. Main category
2. Sentiment analysis
3. Key topics (up to 5)
4. Confidence score (0.0 to 1.0)
Text: \(sanitizedText)
"""
let response = try await session.respond(
to: Prompt(prompt),
generating: ContentClassification.self
)
let content = response.content
await MainActor.run {
self.isProcessing = false
completion(content)
}
} catch {
await MainActor.run {
self.isProcessing = false
let errorMessage = handleSafetyGuardrailsError(error)
self.lastError = errorMessage
completion(nil)
}
}
}
}Analysis Features:
- Multi-dimensional Classification: Category, sentiment, topics, confidence
- Confidence Scoring: Numerical reliability assessment
- Topic Extraction: Identifies key themes in content
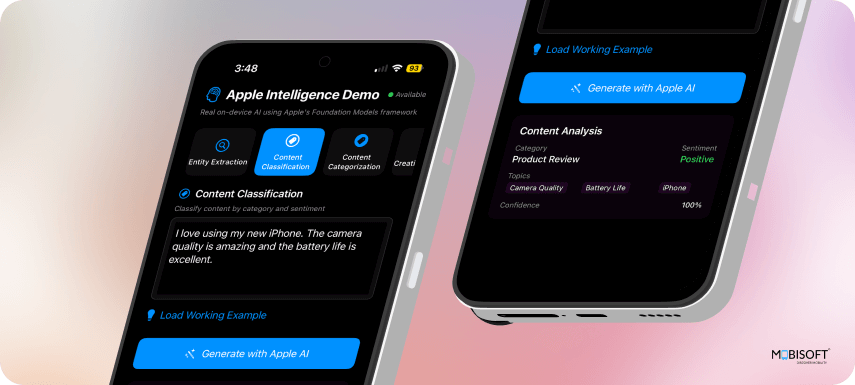
8. Creative Content Generation
func generateCreativeContent(type: CreativeType, prompt: String, completion: @escaping (String) -> Void) {
guard case .available = model.availability else {
completion("Foundation Model not available")
return
}
isProcessing = true
lastError = nil
Task {
do {
let enhancedPrompt = switch type {
case .story:
"Write a creative short story based on: \(prompt)"
case .poem:
"Write a poem inspired by: \(prompt)"
case .dialogue:
"Write a dialogue between characters about: \(prompt)"
case .description:
"Write a vivid description of: \(prompt)"
}
let response = try await session.respond(to: Prompt(enhancedPrompt))
let content = response.content
await MainActor.run {
self.isProcessing = false
completion(content)
}
} catch {
await MainActor.run {
self.isProcessing = false
self.lastError = error.localizedDescription
completion("Error generating creative content: \(error.localizedDescription)")
}
}
}
}Creative Capabilities:
- Multi-format Generation: Stories, poems, dialogues, descriptions
- Style Adaptation: Adjusts tone based on content type
- Enhanced Prompting: Context-specific instructions
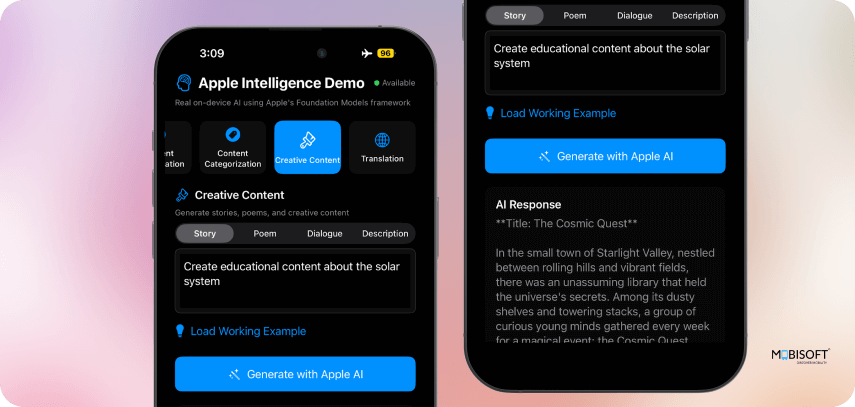
9. Language Processing
Language Detection
func detectLanguage(_ text: String) -> String {
let recognizer = NLLanguageRecognizer()
recognizer.processString(text)
if let language = recognizer.dominantLanguage {
return language.rawValue
}
return "unknown"
}Translation
func translateText(_ text: String, to targetLanguage: String, completion: @escaping (String) -> Void) {
guard case .available = model.availability else {
completion("Foundation Model not available")
return
}
// Sanitize input to prevent safety guardrails
let sanitizedText = sanitizeInput(text)
isProcessing = true
lastError = nil
Task {
do {
let prompt = """
Translate the following text to \(targetLanguage).
Provide only the translation without any additional text or explanations.
Text to translate: \(sanitizedText)
"""
let response = try await session.respond(to: Prompt(prompt))
let content = response.content
await MainActor.run {
self.isProcessing = false
completion(content)
}
} catch {
await MainActor.run {
self.isProcessing = false
let errorMessage = handleSafetyGuardrailsError(error)
self.lastError = errorMessage
completion("Error translating text: \(errorMessage)")
}
}
}
}Language Features:
- Automatic Detection: Identifies the source language
- Context-Aware Translation: Maintains meaning and tone
- Clean Output: Returns only the translation
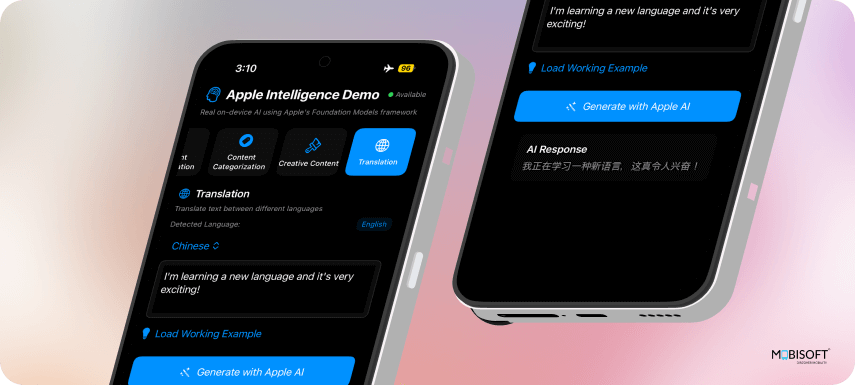
10. Safety and Input Sanitization
Input Sanitization
private func sanitizeInput(_ input: String) -> String {
var sanitized = input.trimmingCharacters(in: .whitespacesAndNewlines)
// Convert to more neutral, educational language to avoid safety triggers
sanitized = convertToEducationalPrompt(sanitized)
// Remove or replace potentially problematic content
let problematicPatterns = [
// Remove excessive punctuation that might trigger safety filters
(try? NSRegularExpression(pattern: "[!]{3,}", options: [])): "",
(try? NSRegularExpression(pattern: "[?]{3,}", options: [])): "",
(try? NSRegularExpression(pattern: "[.]{3,}", options: [])): "...",
// Remove excessive capitalization
(try? NSRegularExpression(pattern: "\\b[A-Z]{5,}\\b", options: [])): "",
// Remove potential spam patterns
(try? NSRegularExpression(pattern: "\\b(click|buy|free|win|prize|offer|deal|discount|sale|limited|urgent|act now|don't miss)\\b", options: [.caseInsensitive])): "",
]
for (regex, replacement) in problematicPatterns {
if let regex = regex {
sanitized = regex.stringByReplacingMatches(in: sanitized, options: [], range: NSRange(location: 0, length: sanitized.count), withTemplate: replacement)
}
}
// Limit input length to prevent overwhelming the model
if sanitized.count > 2000 {
sanitized = String(sanitized.prefix(2000)) + "..."
}
// Ensure the input is not empty after sanitization
if sanitized.trimmingCharacters(in: .whitespacesAndNewlines).isEmpty {
sanitized = "Please provide a valid input for processing."
}
return sanitized
}Educational Prompt Conversion
private func convertToEducationalPrompt(_ input: String) -> String {
let lowercased = input.lowercased()
// Convert creative requests to educational format
if lowercased.contains("write") && (lowercased.contains("story") || lowercased.contains("poem")) {
return "Create educational content about the topic mentioned."
}
// Convert "tell me about" to educational format
if lowercased.contains("tell me about") || lowercased.contains("write me") {
let topic = input.replacingOccurrences(of: "tell me about", with: "", options: .caseInsensitive)
.replacingOccurrences(of: "write me", with: "", options: .caseInsensitive)
.trimmingCharacters(in: .whitespacesAndNewlines)
return "Provide educational information about \(topic)."
}
// For very short inputs, add educational context
if input.count < 15 && input.components(separatedBy: .whitespaces).count <= 3 {
return "Provide educational information about \(input)."
}
return input
}Error Handling
private func handleSafetyGuardrailsError(_ error: Error) -> String {
let errorDescription = error.localizedDescription.lowercased()
if errorDescription.contains("safety") || errorDescription.contains("guardrail") {
return "The content may have triggered safety filters. Please try rephrasing your request with different wording."
} else if errorDescription.contains("inappropriate") {
return "The content appears to be inappropriate. Please provide different content to process."
} else if errorDescription.contains("policy") {
return "The request doesn't meet our content policy. Please try a different approach."
} else if errorDescription.contains("rate limit") || errorDescription.contains("quota") {
return "Too many requests. Please wait a moment before trying again."
} else {
return "An error occurred while processing your request. Please try again with different content."
}
}Safety Features:
- Input Filtering: Removes problematic patterns and excessive punctuation
- Length Limiting: Prevents model overload with long inputs
- Educational Conversion: Converts requests to an educational format
- User-friendly Errors: Clear, actionable error messages
11. Key Implementation Insights
Architecture Benefits:
- Centralized AI Logic: All AI operations in one manageable class
- Reactive UI Updates: @Published properties enable real-time UI updates
- Type Safety: Leverages Swift's type system for AI responses
- Error Resilience: Comprehensive error handling with user-friendly messages
- Performance Optimization: Efficient session management and input processing
Best Practices:
- Always Check Availability: Verify model availability before operations
- Sanitize Input: Clean user input to prevent safety guardrail triggers
- Use Structured Generation: Leverage @Generable for type-safe AI responses
- Handle Errors Gracefully: Provide user-friendly error messages
- Manage State Properly: Use @Published properties for UI updates
- Async/Await: Use modern Swift concurrency for AI operations
- MainActor: Ensure UI updates happen on the main thread
Performance Considerations:
- Session Reuse: Language model sessions are efficiently managed
- Input Limiting: Text input is capped to prevent model overload
- Background Processing: AI operations run on background threads
- Memory Management: Proper cleanup of AI resources
This LocalAIManager implementation provides a solid foundation for building Apple Intelligence apps that can handle various AI operations while maintaining a great user experience and code maintainability. It’s a practical example of how foundation models in Apple can empower developers to deliver intelligent iOS 26 AI features natively within their apps.
Summing It Up
We've walked through building an Apple Intelligence app using iOS 26’s Foundation Models framework. The LocalAIManager handles everything from basic text generation to complex tasks like entity extraction and content classification, all while keeping your code type-safe with @Generable.
The key takeaways are simple: always check model availability, sanitize user input, handle errors gracefully, and use modern Swift patterns. This approach gives you a solid foundation for creating AI-powered iOS apps that work reliably and provide great user experiences using on-device AI and Apple machine learning.
As we look to the future, on-device AI will become even more integral to mobile apps, paving the way for more powerful, efficient solutions. Learn more about the future of mobile app development in 2026.
Access the full source code for this demo on GitHub and start building your own Apple Intelligence applications today!





 October 13, 2025
October 13, 2025


