Introduction
The healthcare industry has become a prime target for cybercriminals due to the vast amount of sensitive patient data. With increasing reliance on digital systems, ensuring healthcare cybersecurity has never been more critical. From Electronic Health Records (EHR) to financial information, a data breach can have severe repercussions, including identity theft, financial losses, and even compromised patient care.
Patient data breaches have become a significant concern globally, with the healthcare sector experiencing numerous cyberattacks in recent years. Here are some notable statistics:
- 2023: The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) reported 725 healthcare data breaches involving 500 or more records, exposing over 133 million records.
Reference website: hipaajournal.com
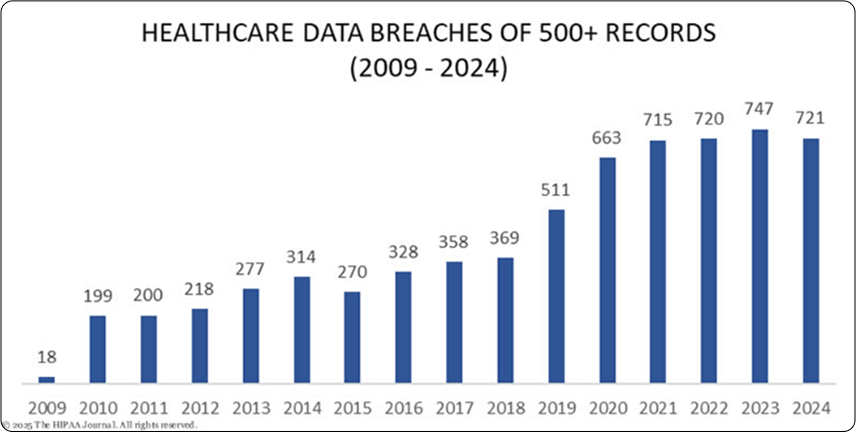
- 2024: The first half of 2024 saw over 43 million breached healthcare data records in the United States.
Reference website: statista.com
- 2024: Thirteen data breaches each affected more than 1 million healthcare records, including the most significant healthcare data breach to date, impacting an estimated 100 million individuals.
Reference website: hipaajournal.com
- Global Impact: In 2024, the global average cost of a data breach reached $4.88 million, a 10% increase from the previous year and the highest recorded to date.
Reference website: ibm.com
Healthcare Data Breach Statistics in India:

- Cyberattack Frequency: India's healthcare sector experiences approximately 6,900 cyberattacks weekly, attributed to outdated technology and limited healthcare cybersecurity funding.
Reference website: indiatoday.in - Recent Breach: In September 2024, Star Health, a leading Indian health insurer, suffered a data breach where a hacker used Telegram chatbots to leak customer data, including medical records and personal identification details.
Reference website: reuters.com - Rising Threats: India has seen a surge in healthcare data breaches, with 1.9 million cyberattacks reported up to November 28, 2022.
Reference website: cybersierra.co
These statistics underscore the critical need for healthcare organizations worldwide to strengthen healthcare cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive patient information.
This blog explores key strategies to enhance cybersecurity in healthcare and protect patient data from breaches.

1. Implement Robust Access Controls

Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC is a security approach that restricts access to patient data breaches based on user roles and responsibilities within an organization, ensuring that only specific people can view or modify sensitive information.
Key Principles of RBAC:
- Role Assignment – Access is given based on predefined roles rather than individual permissions.
- Least Privilege Principle – Users are given only the necessary access to perform their job functions.
- Separation of Duties – Prevents conflicts of interest by ensuring no single user has control over all critical processes.
- Audit & Monitoring – Regularly reviewing access logs helps detect suspicious activities and enforce compliance.
RBAC simplifies compliance with regulations like HIPAA compliance consultant and GDPR by ensuring that sensitive patient data is accessible only to those who need it.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is a measure used to verify the identity of the users before accessing the data which reduces the risk of unauthorized access by adding an extra layer of security.
Types of Authentication Factors in MFA:
- Something You Know – A password or PIN.
- Something You Have – A smartphone, security token, or one-time passcode (OTP) sent via SMS or email.
- Something You Are – Biometric verification such as fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, or retina scanning.
Benefits of MFA in Healthcare:
- Enhanced Security – Even if a hacker obtains a password, they still need the second authentication factor to get access.
- Regulatory Compliance – Helps meet security requirements under HIPAA, GDPR, and HITECH.
- Protection Against Phishing & Credential Theft – Prevents attackers from accessing accounts even if login credentials are compromised.
- User-Friendly Authentication – Modern MFA solutions integrate seamlessly with single sign-on (SSO) systems, reducing login friction.
By implementing MFA, healthcare organizations can strengthen access control measures and protect patient data from cyber threats in the healthcare industry.
2. Encrypt Patient Data

Encryption is useful for sensitive data to convert into unreadable code, making it useless to hackers. Both data at rest (stored data) and data in transit (transmitted data) should be encrypted using advanced encryption standards (AES-256, TLS 1.2/1.3).
Types of Encryption in Healthcare:
- Data at Rest Encryption – Protects stored data, such as patient records in databases or files on servers, by using encryption algorithms like AES-256. This ensures that even if unauthorized access is gained to the storage system, the data remains unreadable without the proper decryption key.
- Best Practices:
- Use strong encryption algorithms (AES-256 is industry standard).
- Implement full-disk encryption for devices that store patient data.
- Secure encryption keys separately from the encrypted data.
- Best Practices:
- Data in Transit Encryption – Secures data being transmitted between systems, such as between a hospital and a third-party provider, using protocols like TLS 1.2/1.3. This prevents unauthorized interception and tampering while data is in motion.
- Best Practices:
- Use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)/Transport Layer Security (TLS) encryption for web-based communications.
- Encrypt emails containing sensitive patient data.
- Implement VPNs for secure remote access.
- Best Practices:
- End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) – Ensures that data remains encrypted throughout its entire journey, from sender to recipient, preventing interception at any stage. This is especially important for healthcare communications, such as doctor-patient messaging and telehealth sessions.
- Best Practices:
- Use E2EE for messaging applications handling patient information.
- Deploy encryption for video consultations in telemedicine.
- Ensure patient portals use E2EE for secure data exchange.
- Best Practices:
Benefits of Encrypting Patient Data:
- Confidentiality – Ensures that only authorized individuals can access patient information.
- Regulatory Compliance – Helps meet security standards like HIPAA, GDPR, and HITECH, which mandate encryption of healthcare data security.
- Data Integrity – Prevents unauthorized modification of patient records, ensuring accuracy and trust in medical information.
- Protection Against Ransomware Attacks – Encrypted data remains unreadable to attackers, reducing the impact of breaches.
Healthcare organizations should implement encryption key management best practices, ensuring keys are stored securely and rotated periodically to prevent unauthorized access. Adopting robust cybersecurity services for healthcare providers can significantly enhance the security of patient data.
3. Regular Security Audits & Risk Assessments
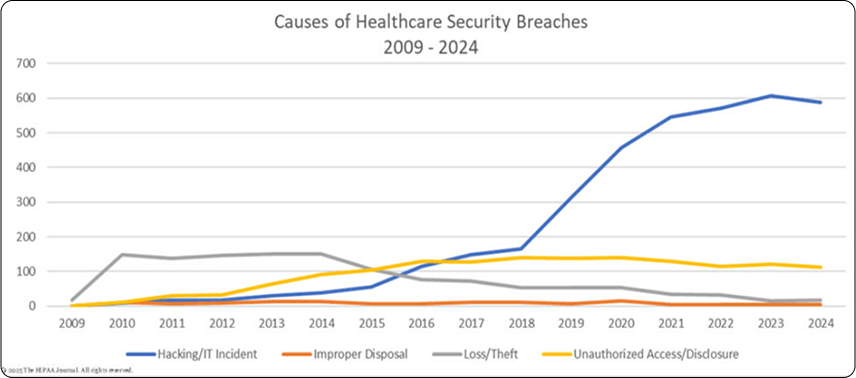
Regular security audits and risk assessments are essential for identifying vulnerabilities in healthcare IT security systems before they can be exploited by cyber threats.
Key Components of Security Audits:
- Penetration Testing – Simulates cyberattacks to evaluate system defenses.
- Vulnerability Assessments – Identifies weaknesses in software, networks, and infrastructure.
- Compliance Audits – Ensures adherence to regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and HITRUST.
- Access Reviews – Verifies that user permissions align with job roles and responsibilities.
- Incident Response Testing – Evaluates the effectiveness of an organization's response to security breaches.
Benefits of Regular Security Audits:
- Early Threat Detection – Identifies risks before they lead to data breaches.
- Regulatory Compliance – Helps meet legal and industry standards for data protection.
- Improved Incident Response – Strengthens an organization’s ability to handle security incidents effectively.
- Enhanced Security Posture – Provides insights for continuous improvements in healthcare cybersecurity frameworks.
Risk Assessments in Healthcare:
Conducting regular security audits helps identify vulnerabilities. Penetration testing and vulnerability assessments should be performed regularly to strengthen security measures.
Steps in a Risk Assessment Process:
1. Identify Assets – Determine what data, systems, and devices need protection. This includes patient records, databases, servers, and medical devices.
2. Assess Threats – Identify potential security threats such as malware, insider threats, phishing attacks, and ransomware.
3. Evaluate Vulnerabilities – Analyze weaknesses in existing security controls, such as outdated software, misconfigurations, or lack of access restrictions.
4. Determine Impact – Assess the potential damage a data breach could cause, including financial losses, regulatory penalties, and harm to patient trust.
5. Mitigate Risks – Implement security measures to reduce vulnerabilities, such as installing patches, enhancing firewalls, enforcing access controls, and strengthening authentication mechanisms.
6. Monitor and Update – Continuously review security measures to adapt to evolving cyber threats. Regular audits and real-time monitoring tools help detect and respond to threats promptly.
By conducting regular security audits and risk assessments, healthcare organizations can maintain a strong security posture and proactively protect patient data from cyber threats.
4. Implement Strong Endpoint Security
Hospitals and healthcare facilities use multiple devices, such as computers, tablets, and medical equipment, all connected to networks. Endpoint security solutions are crucial in safeguarding these devices from cybersecurity threats, ensuring that patient data remains secure.
Key Endpoint Security Measures:
- Antivirus & Anti-Malware Software – Detects and removes malicious software before it can cause damage.
- Firewalls – Monitors and filters incoming and outgoing network traffic to block unauthorized access.
- Intrusion Detection & Prevention Systems (IDPS) – Identifies and mitigates potential threats in real time.
- Device Management & Patching – Ensures that all endpoints are updated with the latest security patches and firmware.
- Zero Trust Security – Implements strict access controls, requiring continuous authentication and verification.
By deploying strong endpoint security measures, healthcare organizations can protect devices and networks from cyber threats, ensuring the safety of patient data in line with healthcare cybersecurity best practices. Learn more from our Securing HealthTech Case Study for a real-world example of how endpoint security was implemented effectively.
5. Employee Training & Awareness

Human error remains one of the leading causes of data breaches in healthcare. Even the most advanced security measures can be compromised if employees are unaware of cybersecurity best practices. Regular training and awareness programs are essential to ensure that all staff members understand how to avoid healthcare data breaches.
Key Aspects of Effective Cybersecurity Training:
1. Recognizing Phishing & Social Engineering Attacks
- Educate employees on common phishing tactics, such as fraudulent emails and fake login pages designed to steal credentials.
- Train staff to identify suspicious emails by checking for unexpected attachments, misspelled sender addresses, and urgent requests for sensitive information.
- Encourage verification of requests through alternative communication channels before taking action.
2. Secure Password Practices & Authentication Protocols
- Require strong, unique passwords for all systems, following best practices like using a mix of uppercase/lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Promote the use of password managers to securely store and manage passwords.
- Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to add an additional layer of security beyond just passwords.
3. Safe Handling of Sensitive Patient Data
- Train staff on proper protocols for storing, accessing, and transmitting patient information.
- Emphasize the importance of logging out of systems when not in use to prevent unauthorized access.
- Ensure that employees follow data minimization principles—only collecting and sharing patient data when necessary.
4. Proper Use of Devices & Networks
- Educate staff on the risks of using personal devices for work-related activities and encourage the use of secure, organization-approved devices.
- Implement Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions to enforce security policies on mobile devices.
- Require employees to connect to secure, encrypted Wi-Fi networks when accessing patient data remotely.
6. Secure Third-Party Integrations
Healthcare organizations frequently use third-party applications and services for electronic health records (EHR) systems, billing software, telemedicine platforms, and cloud storage solutions. However, these integrations can introduce security vulnerabilities if not properly managed.
Best Practices for Secure Third-Party Integrations:
- Vendor Security Assessments – Evaluate third-party providers’ security policies, compliance certifications (e.g., HIPAA compliance, GDPR), and data protection measures.
- Data Access Restrictions – Limit third-party access to only the necessary data and functionalities.
- Encryption & Secure APIs – Use encrypted data exchanges and secure API gateways to prevent unauthorized access to healthcare data.
- Continuous Monitoring – Regularly audit and monitor third-party activities to detect potential threats or policy violations.
Ensuring robust security measures for third-party integrations helps maintain data integrity, compliance, and protection against external cyber threats. For a detailed overview of healthcare data management and its associated challenges, read our Healthcare Data Management: What It Is, Its Challenges, and Opportunities blog post.
7. Backup Data Regularly
Regular data backups are an important component of healthcare cybersecurity, ensuring that patient records and critical system data can be recovered in case of cyberattacks, accidental deletions, or system failures. A well-structured backup strategy helps healthcare organizations maintain data integrity and business continuity.
Key Best Practices for Data Backup in Healthcare:
- Automated & Scheduled Backups – Implement automated backup solutions that regularly store copies of patient records, system configurations, and other critical data without manual intervention.
- Offsite & Cloud Backups – Maintain backups in multiple locations, including secure cloud storage and offline, offsite locations to protect against ransomware attacks or local system failures.
- Encryption of Backup Data – Ensure that both stored and transmitted backup data are encrypted to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Testing & Validation – Periodically test backup systems to ensure data can be successfully restored in case of an emergency.
- Versioning & Retention Policies – Maintain multiple versions of backups for a defined period to allow for recovery from different points in time.
- Disaster Recovery Planning – Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan (DRP) outlining the steps to restore data and systems quickly in case of a cyber incident.
Benefits of Regular Data Backups:
- Protection Against Ransomware – Ensures that patient data can be restored without paying a ransom in case of an attack.
- Data Integrity & Compliance – Supports regulatory requirements such as HIPAA and GDPR, which mandate data protection and recoverability.
- Business Continuity – Minimizes downtime and ensures that healthcare operations continue without disruption.
- Safeguards Against Human Errors – Allows for data recovery in case of accidental deletion or corruption.
By implementing a robust backup strategy, healthcare organizations can significantly reduce the risks associated with data loss and cyber threats, ensuring the security and availability of patient information.
8. Monitor & Respond to Security Threats
Proactively monitoring and responding to security threats is essential to protect patient data from cyberattacks. Cyber threats, such as malware, ransomware, phishing, and insider breaches, are constantly evolving, making real-time threat detection and response a critical component of healthcare cybersecurity.
Key Strategies for Threat Monitoring & Incident Response:
1. Implement Security Information & Event Management (SIEM) Systems
SIEM solutions collect and analyze logs from different sources (firewalls, servers, applications, and network devices) to detect unusual activities and potential threats.
- Benefits:
- Real-time threat detection and alerts.
- Centralized logging for easy forensic analysis.
- Compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and other regulations.
2. Intrusion Detection & Prevention Systems (IDPS)
IDPS monitors network traffic for suspicious activities and blocks potential attacks.
- Types of IDPS:
- Network-Based (NIDS) – Monitors network traffic for anomalies.
- Host-Based (HIDS) – Protects individual devices by analyzing logs and system behaviors.
3. 24/7 Security Operations Center (SOC)
A dedicated SOC team continuously monitors for threats, investigates incidents, and coordinates response actions.
- Key SOC Functions:
- Threat intelligence and attack analysis.
- Rapid response to security breaches.
- Coordination with IT teams for remediation.
4. Automated Threat Response & Incident Management
Automating security response mechanisms reduces the time between detection and mitigation.
- Effective Measures:
- Automated blocking of malicious IP addresses.
- AI-driven analysis for faster detection.
- Endpoint detection & response (EDR) for rapid containment.
5. Establish an Incident Response Plan (IRP)
A well-defined Incident Response Plan ensures a structured approach to handling security breaches.
- Incident Response Steps:
- Detection & Analysis – Identify the breach and assess its severity.
- Containment – Isolate affected systems to prevent further spread.
- Eradication – Remove malware, patch vulnerabilities, and update security controls.
- Recovery – Restore systems and validate security measures.
- Post-Incident Review – Analyze the root cause and improve defenses.
6. Conduct Regular Threat Simulations & Drills
Simulated cyberattacks (e.g., phishing tests and penetration testing) help organizations assess their response capabilities and enhance staff preparedness.
By actively monitoring and responding to cyber threats, healthcare organizations can mitigate risks, reduce downtime, and ensure the protection of patient data against ever-evolving security challenges in the realm of healthcare cybersecurity.
9. Secure Network Infrastructure
A secure network infrastructure is fundamental to protecting healthcare systems from cyber threats. Since healthcare facilities rely on interconnected devices, electronic health records (EHR) systems, and cloud-based services, safeguarding the network from unauthorized access and cyberattacks is essential.
Key Strategies for Securing Network Infrastructure:
- Network Segmentation – Divide networks into smaller, isolated segments to limit unauthorized access. For example, separate medical devices, administrative systems, and guest Wi-Fi to prevent lateral movement by attackers.
- Firewalls & Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) – Deploy firewalls and IDS/IPS (Intrusion Prevention Systems) to monitor and filter network traffic, blocking potential threats before they reach critical systems.
- Secure Wi-Fi Networks – Use WPA3 encryption for wireless networks, restrict guest access, and implement strong authentication for internal Wi-Fi connections.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) – Ensure secure remote access for healthcare professionals by encrypting data transmission between remote users and hospital systems.
- Regular Network Audits – Continuously assess network configurations, scan for vulnerabilities, and update security policies to adapt to emerging threats.
By implementing these measures, healthcare organizations can create a strong defense against cyber threats, ensuring that patient data and critical systems remain protected from unauthorized access and breaches.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity in healthcare is no longer optional—it is a necessity. Implementing these strategies can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches, ensuring patient privacy and HIPAA compliance with regulations. With cyber threats evolving constantly, proactive measures and ongoing vigilance are key to safeguarding healthcare data.
By prioritizing healthcare cybersecurity, healthcare organizations can build trust with patients and provide a safer, more secure digital healthcare experience.

No related posts found.



 March 19, 2025
March 19, 2025


