Today, we witness higher violence rates, bullying, and medical crises during public and school transportation. Safety of riders and students comes first during such times. The first 9 months of 2025 witnessed 11 school shooting incidents in the US. They resulted in 38 injuries and even 4 casualties. Violence is prevalent in various modes of transport, which is why immediate assistance is needed in buses, trains, and other public transport, especially for students.
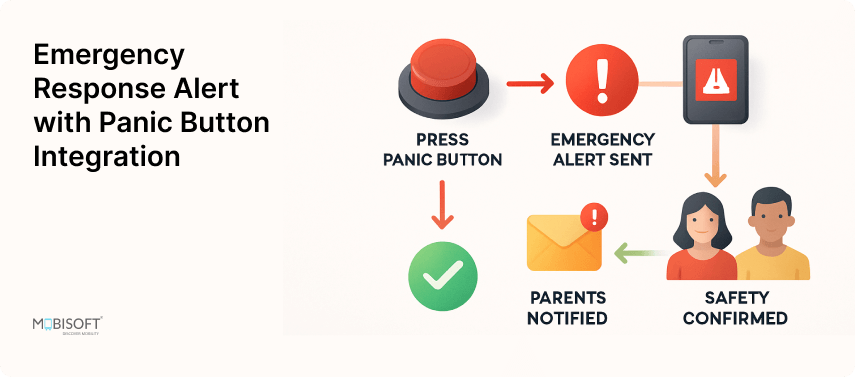
Under such circumstances, panic buttons are valuable safety measures. These buttons encompass wearable devices, smartphone applications, and fixed systems that allow individuals to rapidly summon emergency services. With a quick and discreet means of communicating, panic buttons enhance the general safety of mass and school transportation systems.
Panic buttons for buses and school buses are valuable safety tools for bus and school transportation. They assist in receiving rapid responses as well as bring a state of mind of being prepared and resilient during an emergency.
Learn more about school bus safety features here: school bus tracking and safety features.
The Evolving Future of Safety in Transportation
Historical Context of Safety in Public and School Transportation
Everyone has always been concerned with transportation safety, yet certain mass incidents strengthened such concerns. Mass shootings like the tragic Sandy Hook Elementary School shooting of 2012 and the one at Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School of 2018 altered American laws and public policy. Many states have made legislation mandating upgraded safety features since the tragedies. Examples of such features are installing panic button systems in schools.
These bills demonstrate the importance of safety issues. Alyssa's Law, for example, mandates silent panic alarm systems at public schools with the intent of assuring quick notification of law enforcement during a crisis. These kinds of laws indicate a national change toward a faster response time during an emergency and the protection of students and teachers.
Current Statistics on Safety Concerns in Transportation
The statistics of safety occurrences of school buses and public transportation systems are alarming. According to a law firm, there were 976 fatal school bus accidents between 2013 and 2022. Approximately 108 people are killed and 13,200 people are injured in school bus accidents each year.
Furthermore, studies also show that quick responses can spell a world of difference in survival rates during crises. For example, the chances of surviving a heart attack are lowered with each passing minute of delay before CPR can be applied. With the lives of innocent students on the line,, the use of panic buttons in school buses and public transportation has become a necessity. Institutions that have already implemented panic button systems for school buses witness much fewer incidents. Students report faster response times, feeling safer in schools and buses.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Safety
New technologies are improving the way of keeping individuals safe. Incorporation of panic button technology for buses and schools into existing safety equipment is a significant upgrade. Such buttons are easily integrated into security cameras, communications systems, and business continuity plans so that safety initiatives can function more harmoniously.
Adoption of wearable technology, mobile apps, and fixed panic button systems is just a few of the ways technology is being utilized to upgrade safety features. Schools in California are using the CENTEGIX CrisisAlert System that outfits staff with wearable panic buttons as a means of triggering instantaneous alerts during an emergency. These kinds of initiatives illustrate the point where technology is more than an added value proposition, but a requirement of the changing world of transportation safety technology.
Explore educational transportation software that supports these safety initiatives.

Understanding Panic Buttons: Functionality and Features
What Are Panic Buttons and How Do They Work?
Panic alarms are instant alarm systems that notify security personnel, police officers, or the assigned teams about an emergency. There are three varieties of each type: wearable devices, phone applications, and fixed systems at a location or vehicle.
- Wearable Devices: These are often tiny wearable buttons that can be attached to garments or used as accessories. These allow individuals to silently summon assistance discreetly.
- Mobile Applications: The majority of panic button systems are nowadays offered as phone apps that one can download. Phone apps are often accompanied by features that allow you to activate rapid alarms to specific contacts, as well as law enforcement.
- Fixed Systems: Some areas, like classrooms, buses, or mass transportation systems, are also equipped with fixed panic buttons for security. When activated, they instantly notify law enforcers or guards.
Key Features of Modern Panic Buttons
Present-day panic buttons are loaded with advanced high-tech features that make them much more effective:
- Instant Alerts: Panic buttons will trigger instant alerts to emergency services, ensuring that aid is sent right away.
- Location Tracking: Most panic button systems are equipped with GPS functionalities that assist the rescuers in locating the specific location of the distressed user.
- Silent Operation: Some systems can send quiet alerts. This helps the authorities have information, bypassing possible threats.
Some of the best panic button systems for buses and schools are the Rave Panic Button and the Silent Beacon. They are both utilized in a variety of schools and mass transit systems.
Integration with Existing Safety Systems
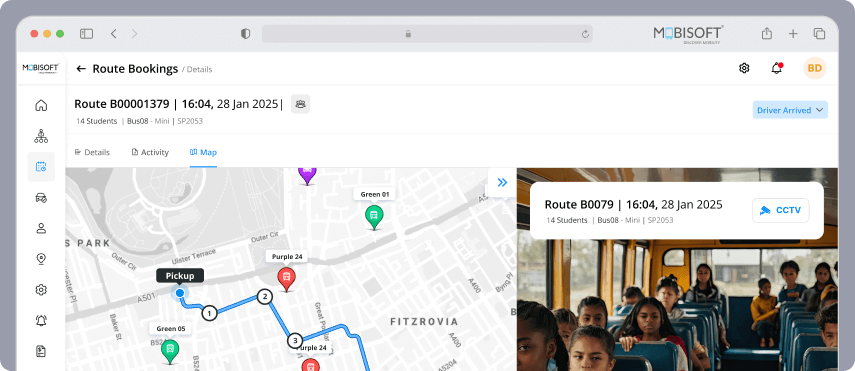
The effectiveness of panic buttons is much enhanced once they are integrated with other established safety features such as surveillance cameras, alarm systems, and information networks. With the use of an all-encompassing integrated safety system, panic buttons in public transportation and school buses may handle a multi-faceted response during emergencies, considering all aspects of safety.
For example, CCTV cameras at the location of panic button activation send a live feed of the incident. This greatly helps the response team in analyzing the situation. This level of technology integration immensely reduces the effort and time taken to respond. Also offering important insights in the meantime.
Find out more about bus transportation software solutions for enhanced safety and efficiency.
Case Studies: Successful Implementations of Panic Buttons
Schools: A Focus on Recent Initiatives
Panic buttons for school buses are more effective when combined with other safety features such as surveillance cameras, alarm systems, and communication systems. When these elements work together, panic buttons create a complete safety setup, allowing a multi-level response to emergencies while addressing all aspects of school transportation safety features.
For example, a panic button may trigger cameras to immediately begin recording what is unfolding, and systems of communication may dispatch vital information to first responders. This connection also works at reducing confusion and accelerating response time during emergencies.
Public Transportation: Real-World Applications
In California, the Covina-Valley Unified School District implemented the CENTEGIX CrisisAlert System, providing staff with wearable panic button devices. This portability allows users to immediately trigger alarms, be it physical harm or gun violence. As a result, the students could get help instantly, creating a much safer environment, stated superintendent Dr. Elizabeth Eminhizer. The reason behind this safety also lies in the fact that these systems also alert the local police. This shows how panic button technology for buses and schools protects the well-being of students.
Comparative Analysis: Schools vs. Public Transport
Educational institutions and mass transit systems are complex in their own ways, yet both effectively use panic button systems. Both rely on rapid communication and fast response. The difference lies in the circumstances: schools primarily focus on child safety and behavioral issues, while public transportation handles broader safety concerns, including crime and medical emergencies.
Check out transportation safety and logistics solutions to enhance your transportation safety measures.
The Legal Framework Supporting Panic Buttons

Overview of Laws Mandating Panic Buttons
Several laws mandate the use of panic buttons in school buses, resulting in growing demands. A good example of this is Alyssa’s Law, which states that the use of silent panic alarms is a must in public schools. States like Texas, Florida, and New Jersey also have such laws to effectively communicate danger to the concerned authorities..
Impact of Legislation on Safety Measures
Laws have necessitated the integration of panic button systems for school buses, with numerous jurisdictions indicating improved emergency response times. Educational institutions that have adopted these systems report enhanced preparedness for emergencies and an increased focus on safety measures. The incorporation of panic buttons into the safety protocols for school transportation is presently regarded as a fundamental component of emergency preparedness.
Challenges in Compliance and Implementation
Even though legislation has enhanced safety, issues still exist. Prices for panic button systems on buses and in schools can be expensive, and enforcing the level of care can be challenging when access to technology is limited or when training programs for staff and students are nonexistent.
Learn more about panic buttons and emergency response systems.
Challenges and Considerations for Implementation
Technical Challenges in Deploying Panic Buttons
Deployment of panic button systems for school buses and public transportation also faces a variety of challenges. Technological complications such as connectivity, User Interface compatibility, and interfacing with already installed safety systems could compromise their operational effectiveness. For example, panic buttons should be able to function consistently and automatically under high-stress situations and thus should receive serious consideration of configuration and design.
Training and Preparedness of Staff and Students
At times when a panic button in school buses or mass transit might be needed, anxiety and stress can easily take over. Thorough training and situational awareness are important beforehand. Panic buttons for buses and schools are successful not only because of the technology involved, but also because of the individual preparedness of staff and students.
Public Perception and Skepticism
Some support the use of panic button technology for transportation, and others are hesitant. Critics note that relying solely on technology may create a false sense of security and draw less attention to human response training. To handle these issues, there should be an open forum regarding how panic button systems are part of a complete safety plan.
Financial Implications for Schools and Transportation Authorities
The cost of panic button systems for school buses and public transportation, including acquisition, installation, and upkeep, can sometimes be high. Schools and transportation networks must weigh costs against the possible benefits of enhanced protection and reduced litigation exposure during emergencies.
For additional insights, see how student safety in school transportation is enhanced through integration with modern technology.
The Future of Panic Buttons in Safety Protocols
Emerging Trends in Panic Button Technology
The integration of panic buttons in schools and buses as part of a comprehensive safety plan improves security management. Using a combination of cameras, communication, and emergency alert systems on school buses, we can provide a secure environment among students and passengers.
Potential for Expanding Use Beyond Schools and Public Transportation
Apart from their existing use, the prospects of extending the use of panic buttons into other settings. Offices, festivals and celebrations, and medical facilities have immense uses. With increasing safety issues emerging across the sectors, technologies of panic buttons could become a vital mitigant of risks.
The Importance of Continuous Innovation in Safety Measures
To keep them useful, the safety measures have to evolve as new threats develop. Collaboration between technology companies and government safety organizations ensures that panic button technology for buses and schools is always relevant and effective.
Vision for a Safer Future: A Comprehensive Smart Safety Ecosystem
Incorporating panic buttons in public and school transportation as part of a broader safety plan enhances security management. Using a combination of cameras, communication systems, and emergency alert systems for school buses, we can create a safer environment for students and passengers.
Explore panic buttons for women’s safety in transportation as an additional safety application.
Conclusion
In a 2025 survey of school and district staff, 76% identified student safety as a top priority for school transportation, highlighting growing awareness of safety concerns. Panic buttons for buses and schools are vital safety devices, ensuring that help is promptly available during emergencies. Panic button systems have proven records for improving safety among students. This is why support from the government and technological upgrades are necessary for better implementation.
School authorities, drivers, law bodies, and parents should all urge for mandatory implementation of panic buttons for school buses and public transportation. This safety is crucial for students who can’t focus because of such dangers. anic button solutions are highly beneficial investments, safeguarding the lives of young students and the general public during mass transportation.
Key Takeaways:
- Rising Safety Concerns: With bullying and gun violence incidents in schools and buses, panic buttons are now essential for student and rider safety.
- Panic Buttons Defined: Panic buttons come in various forms: mobile apps, wearable devices, or fixed systems. They help the user to secretly notify the assigned teams to send instant help.
- Technology Integration: Modern panic buttons are embedded with GPS systems, communication channels, and surveillance. This ensures swift and effective responses.
- Legislative Support: Laws like Alyssa’s Law mandate silent panic alarms in schools, accelerating adoption and emphasizing rapid emergency response.
- Real-World Effectiveness: students feel safer with panic buttons because of quick response rates, report schools.
- Implementation Challenges: inadequate training, technical setup, implementation costs, and public skepticism still obstruct the effective deployment and use of panic buttons.
- Future Trends: starting with schools, panic buttons should be deployed in all public transport. Integration with AI and cloud systems will further improve efficiency.
- Strategic Recommendation: Organizations are investing significantly. However, the adoption of panic button technology for school buses and public transportation still requires mandatory laws, knowledge among schools and students, and aided support by the government to make mass transit safer.





 September 11, 2025
September 11, 2025


