In the race to MVP, UX design often takes a backseat to functionality. You prioritize getting the thing to work fast. But when it’s time to scale, that UX debt becomes dangerous.
Inconsistent design, inaccessible interactions, and confusing flows don’t just hurt user experience; they hurt growth. Before you scale your product, you need to stop and ask if your UX health is strong enough to grow with you? And most of the time, the answer is a big NO.
So, What is UX Health?
Nowadays, almost all businesses understand UX or at least know the term User Experience (UX). But is it enough to just know UX or to work on your product once with the perspective of UX?
UX health check is not a one-time fix; it is a continuous UX evaluation process. You need to revisit it regularly, make the required improvements, and ensure it runs smoothly for your users and indirectly for your business.
88% of users won’t return after a bad experience (Source: designrush.com). UX improvements can cut support costs by 30–50%, as fewer users need help to complete tasks (Source: Nielsen Norman Group). Around 24% of users depend on accessibility features (Source: BanklessTimes, 2024).
UX health usually refers to the overall state and quality of a product’s user experience at a given time. Understanding the UX health helps determine if the product or service is compatible for the current time and adaptable for the future.
A product’s or service’s UX health is determined by the following parameters:
- Is your product usable?
- Is it consistent across the flows?
- Is it trustworthy while performing?
- Are there any accessibility issues?
- Is it really solving the problem of your target audience?
- Is it secure enough?
- Is your product/service inclusive of your target audience’s sub-categories?
Explore how a structured UX approach can strengthen your product’s foundation with our Comprehensive UX Design Audit Services.

Why Should You Check The UX Health of The Product?
There are numerous reasons to perform a User Experience Audit, but only one reason not to let the product die eventually.
Let's see a few important reasons to check the health:
- Want to upgrade the system, major redesign, or rebrand
- Try to reach a wider target audience
- Want to penetrate the market from a new geography & demography
- Want to keep up with the current pace
- Make the product compatible with newer technology
- Or just want to give the best experience to the users and build the brand with a loyal customer base.
Your reason can be any one, but it is important to conduct a UX design audit periodically.
How To Identify If The Scaling Product Is Going In The Right Direction?

Whenever a business wants to scale its product or services, checking if they are going in the right direction or not is very important. Meaning if the business wants a product to cater to the new target audience, which is elderly people who understand only the local language, then the UX should consist of good contrast, straightforward & minimal UI, bigger font size, an option to change language & appropriate gesture controls.
If all or many of the things from the previous list are absent or can’t be accommodated easily & business is more focused on other things, then that product is not going in the right direction, and will inevitably not work.
Parameters to check the direction:
- Define a clear goal for scaling the product or service
- Identify, define & empathize with the target audience
- Structure features as per users' needs
- Check if the current product or service can have room to easily accommodate the changes for new features.
The first three points are straightforward, but for the fourth, businesses need to invest the most effort, time, and budget. To identify gaps and possibilities in the product, which determine its UX health going forward, businesses must conduct a design audit or UX audit.
To make your scaling process more effective, explore our Design System Consulting for Scalable Products.
What is a UX Design Audit?
In simple words, a Design Audit is a systematic approach to evaluate a product’s visual parameters and user experience to ensure consistency, usability, and alignment with brand and business goals. A UX Design Audit helps identify gaps and the current state of the product.
What exactly is covered under the design audit:
- Survey questions & findings
- Competitors analysis
- User demographics, Google Analytics & Conversion rate
- Heat map & Click map
- User Behaviour & Funnel Analysis
- Visual Consistency, Interaction & Navigation audit
- Performance, Cross-Platform & Device Testing
- User persona & User flows analysis
- UX Heuristic Evaluation
- Review of accessibility & Inclusivity
Don’t get overwhelmed by the big list. While conducting a UX audit, not all parameters may apply. It depends on the business goal and product lifecycle stage.
For instance, if the product is at an early stage, you may not get enough data on demographics, analytics, or funnel analysis. Or if the goal is to identify accessibility gaps, parameters like Visual Consistency, Interaction, Navigation audit, UX Heuristic Evaluation, and Accessibility Review will be more relevant.
While parameters may vary, certain key ones Performance analysis, Navigation audit, Heuristic Evaluation, and Accessibility & Inclusivity Review, should always be included during a UX Design Audit to evaluate the product’s UX health.
You can learn more about optimizing design for scaling by reading our Comprehensive UX Design Process Guide.
Step-by-step Guide to Do a UX Audit
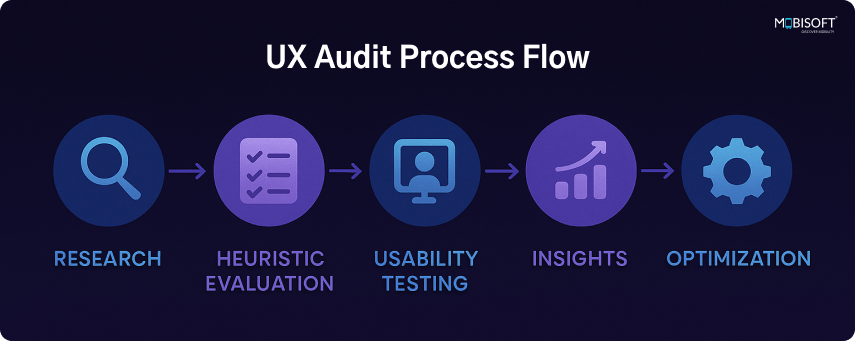
1. Prep & Kickoff
- The goal is to align audit scope, KPIs, stakeholders, and access.
- Get access to Google Analytics/GA4, heatmap tool (Hotjar/FullStory/Contentsquare), product analytics (Mixpanel/Amplitude), design files, and staging credentials.
- List primary business goals and success metrics
- Deliverable: UX Audit Checklist brief + Credentials & accesses.
2. Stakeholder Interviews & Surveys
- The goal is to understand business priorities, constraints, and user complaints
- Take short interviews around 15-30 minutes with all relevant stakeholders.
- Keep the questions open-ended but focused on the subject.
- Ask primary user problems, top funnels, known pain points, and recent changes.
- Conduct quantitative surveys if needed to understand common issues.
- Ask closed-ended questions like multiple-choice questions in quantitative surveys
- Try to cover all groups of demography & geography of the target audience.
- Summarize the findings.
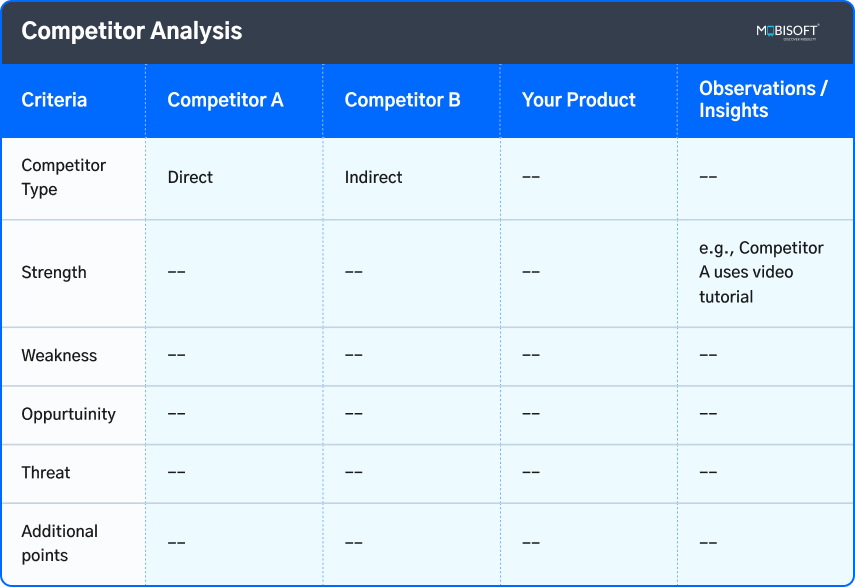
3. Competitor Analysis
- The goal is to understand Benchmark features, UX patterns, pricing, and market gaps.
- Select 4–6 direct & indirect competitors. As per the business goal & marketing strategy, you can segregate the local & global market.
- Use the SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities & Threats) method to do competitor analysis. You can add more factors to this method as needed
- Avoid making it too lengthy, and with a larger competitor pool.
4. User Personas & User Flows Analysis
- User Persona is a method to translate the theoretical target audience into a visual identity & by considering this virtual user, create user flow for each feature. Example, Sign in to onboarding a new user OR Search product to checkout.
- Consider the following parameters in the user persona: Basic information (age, gender, marital status, location, etc), Bio, Frustrations, Goals, Personality, Familiarity with devices, Familiar brands. Create personas as real as possible.
- For multiple target audiences, we can create multiple user personas, but the key is to create personas that cover important categories of the target audience.
- Start with the happy path in the user flow, but expand it with fallback options & corner cases to cover all the important scenarios.
- Deliverable: Persona cards + annotated user flows showing structured flow diagram & friction points.
5. User Behavior, Demographics & Funnel Analysis
- This step in the UX Evaluation Process helps identify where users drop off, who they are, and the conversion rate.
- Understand acquisition channels: organic, paid, referral & conversion per channel.
- Analyze page load speed, traffic patterns & bounce rates
- Check user Behavior with a seasonal, geographical, and demographical perspective & identify dead-ends.
- Map funnels ideal flow Vs how currently implemented.
- Get step-wise abandonment rates.
- Extract statistics from the above data to reach the conclusion & create hypotheses (e.g., “form is too lengthy so users abandon the process” or “price not visible on checkout page so users get confused”, etc).
6. Heatmap & Clickmap Analysis
- A critical component of a UX Design Audit, this analysis identifies user attention, dead clicks, and interaction patterns.
- Capture scrolling style & stops, calculate clicks to complete the flow, example: Search Product to checkout.
- Look for missed CTAs & clicks
- Correlate heatmap insights with analytics (e.g., User clicks on non-clickable elements = confusion).
- Take a separate note of all the analysis
7. Performance, Cross-Platform & Device Testing
- The goal is to ensure speed, reliability, and consistent experience across devices/browsers.
- Run UX Audit Tools such as Lighthouse or WebPageTest for performance metrics (CLS, LCP, FID, or TTFB).
- Test on representative devices (iOS/Android, low-end Android, desktop) and browsers.
- Check offline & low network behavior and error handling.
- Evaluate image sizes, lazy loading, bundle sizes, and third-party script impact.
- Deliverable: Performance report with issues and solutions
8. Visual Consistency, Interaction & Navigation Audit

- The goal is to ensure UI consistency, clear affordances, and clear navigation
- Check for inconsistencies in typeface, font scale, spacing, color tokens, iconography, alignments, button sizes & states (hover, disable, pressed, etc).
- Check for global nav, search, filters, breadcrumbs, and back behavior.
- List the inconsistencies with screenshots and create a prioritization list to fix the inconsistencies.
Dive deeper into professional evaluations with our Web UI/UX Design Services.
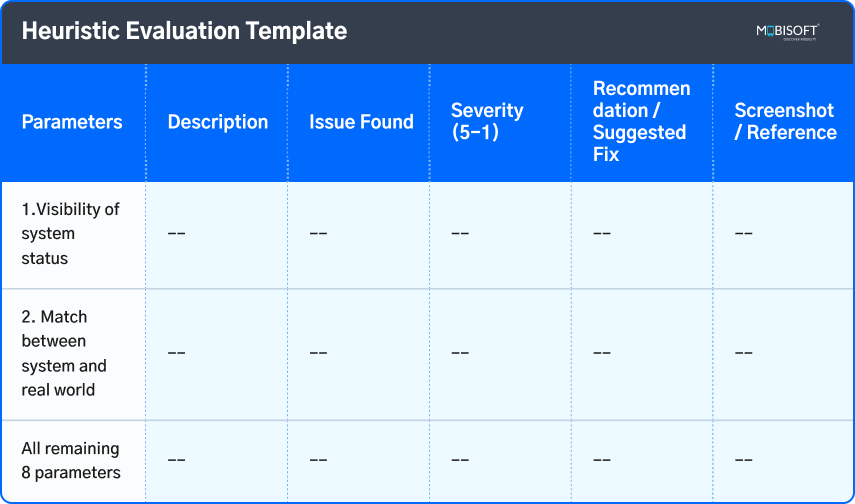
9. Heuristic Evaluation
- This UX Heuristic Evaluation is a usability inspection method used to identify problems in UI and UX design by examining it against recognized usability principles created by Jakob Nielsen.
- Checklist of 10 principles of Heuristic Evaluation:
- Visibility of system status – The system should always inform users about what is going on at every stage.
- Match between system and the real world – Speak the users’ language and follow real-world conventions. Example, use microcopy, patterns, icons, or colors that match with target audience’s real world
- User control and freedom – Provide undo, redo, and easy exits from unwanted states.
- Consistency and standards – Use the same design style & patterns throughout the application. Follow industry conventions.
- Error prevention – Design to prevent errors before they occur.
- Recognition rather than recall – Make options and actions visible; reduce memory load. Make it simple & recognizable so the user does not need to stress his/her memory. Example: icons like save, stop, and left-right arrows.
- Flexibility and efficiency of use – Allow both novice and expert users to operate efficiently.
- Aesthetic and minimalist design – Keep interfaces clean and focused on essentials.
- Help users recognize, diagnose, and recover from errors – Use clear error messages and suggestions.
- Help and documentation – Provide easily searchable help content.
Create a UX Audit Checklist spreadsheet, add screenshots per module, and give severity scoring to each parameter.
10. Accessibility & Inclusivity Review
- The aim is to make sure the product works well for people with disabilities and in different situations.
- Run automated or manual tests to check the accessibility
- Automated tests: axe DevTools / Lighthouse / WAVE for WCAG
- While checking manually, you can use the following checklist
- Keyboard navigation
- Focus order for actions
- Alt text for images
- ARIA attributes
- Text and UI element contrast ratios (min 4.5:1 for normal text).
- Plain language, avoid jargon, meaningful link text.
- Form fields (gender optional), location/time formats, currency handling, and multiple language support
- Deliverable: Accessibility report (auto + manual) with WCAG priority fixes.
So What’s Next?
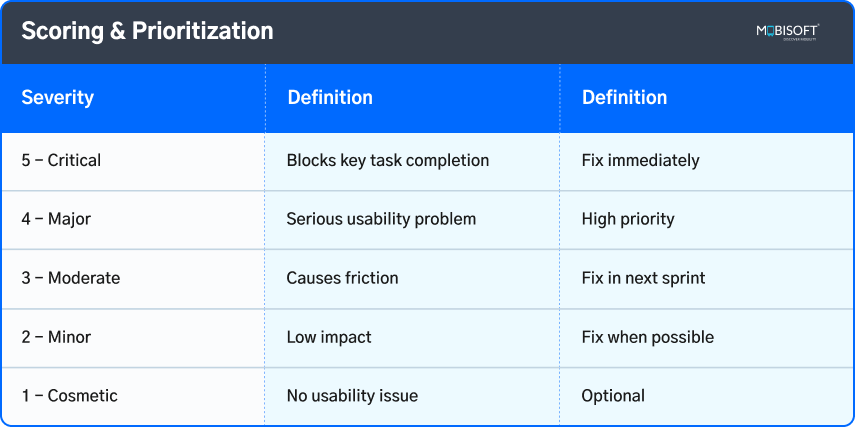
After collecting all the information from earlier actions, analyze and rank the problems based on severity scores. Create a clear plan to make the needed changes.
It’s a time-consuming but critical task; skipping it reduces the value of your Design Audit or Product Design Audit.
Explore how design decisions impact conversion in our guide How User Experience Impacts Conversion Rates.
Template & Checklist for Quick Execution (Bonus)
Check out the following UX Audit Template & Checklist you can directly use it during UI/UX Audit Services or usability evaluations.
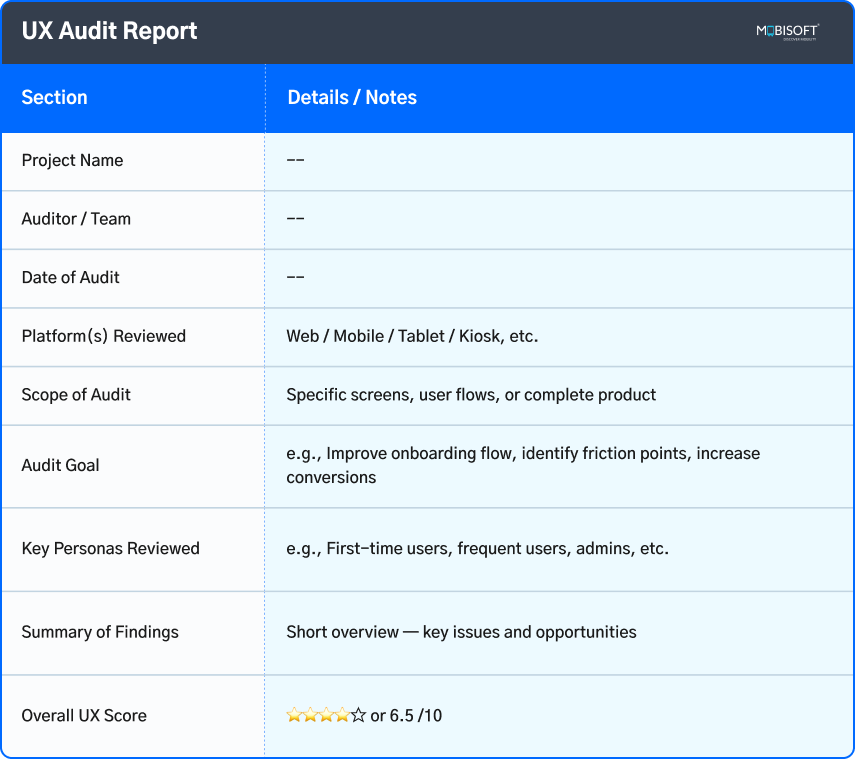
1. UX Audit report
2. Competitor Analysis
3. Heuristic Evaluation Template
You can use the same template for Accessibility & Inclusivity Review
4. Scoring & Prioritization
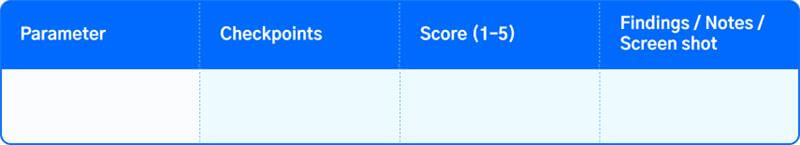
5. For all other analyses, like Visual Design & Consistency, Content & Communication, or Performance & Technical
Want to enhance your usability testing approach? Explore our insights on Usability Testing Best Practices.
Conclusion
Identifying UX health for your product is a crucial task before going ahead. A design audit is the process that helps evaluate the UX health by applying step-by-step parameters. Initially, it may feel overwhelming or a time-consuming process, but its benefits are far more important for business while going ahead in the product's evolution process.
It is a deliberate pause to understand how people truly experience your product. It reveals what analytics alone cannot, such as moments of hesitation, frustration, or quiet satisfaction that users often overlook. Over time, these audits stop feeling like formal exercises and begin to act as a rhythm that keeps your product grounded and alive.
Each finding adds a fresh layer of clarity, helping teams make improvements that are not only functional but also deeply considerate of real user needs. When this practice becomes routine, it cultivates awareness, empathy, and a quiet kind of precision that helps products grow with purpose instead of accident.
Discover how UX influences overall business success in our article: How User Experience Impacts Conversion Rates.
Key Takeaways
- Product success depends on maintaining a consistent user experience.
Design Audits uncover usability issues, visual inconsistencies, and accessibility gaps that daily testing may miss. - Regular UX audits ensure products stay relevant and aligned with evolving user needs and technologies.
- User Experience Audits aren’t about blame they help teams understand real user behavior.
- Including accessibility in every UX Design Audit ensures inclusivity and trustworthiness.
A detailed UX Audit Checklist provides clear guidance for immediate fixes, refinements, and strengths.

FAQs
How can you tell when it’s the right time to run a UX audit?
As soon as you start witnessing lags or glitches, it is time for an audit. Track user engagement and reviews. These are signals for a comprehensive check. Running an audit will provide clarity on what functions well, emerging issues, and aspects that need to change to improve user experience.
How is a design audit different from a full redesign?
They are both parts of the same process. Design audits are check-ups that help identify bottlenecks. Redesigning involves implementing changes to improve upon the existing interface. Some firms redesign without audits, unaware of important issues to address. This results in confusion and an inefficient redesign.
How do UX audits contribute to growth?
Good design brings rewards. When users navigate your product smoothly, engagement increases, churn decreases, and customer loyalty strengthens. A detailed UX audit identifies problem areas and helps refine user interactions to make every touchpoint efficient and effective.
Who should take part in the audit process?
Design audit requires technical knowledge, but it goes beyond developers. Stakeholders, managers, customer support staff, and sales team should all actively take part. Their individual experience and expertise bring out details that make an application stand out.
Should accessibility always be audited?
Absolutely. Accessibility isn’t just a checklist; it’s a responsibility. Every UX audit should include accessibility checks to uncover barriers that prevent people from using your product. Fixing these small issues not only improves inclusivity but also strengthens your brand’s trust and credibility.



 November 5, 2025
November 5, 2025


